 |
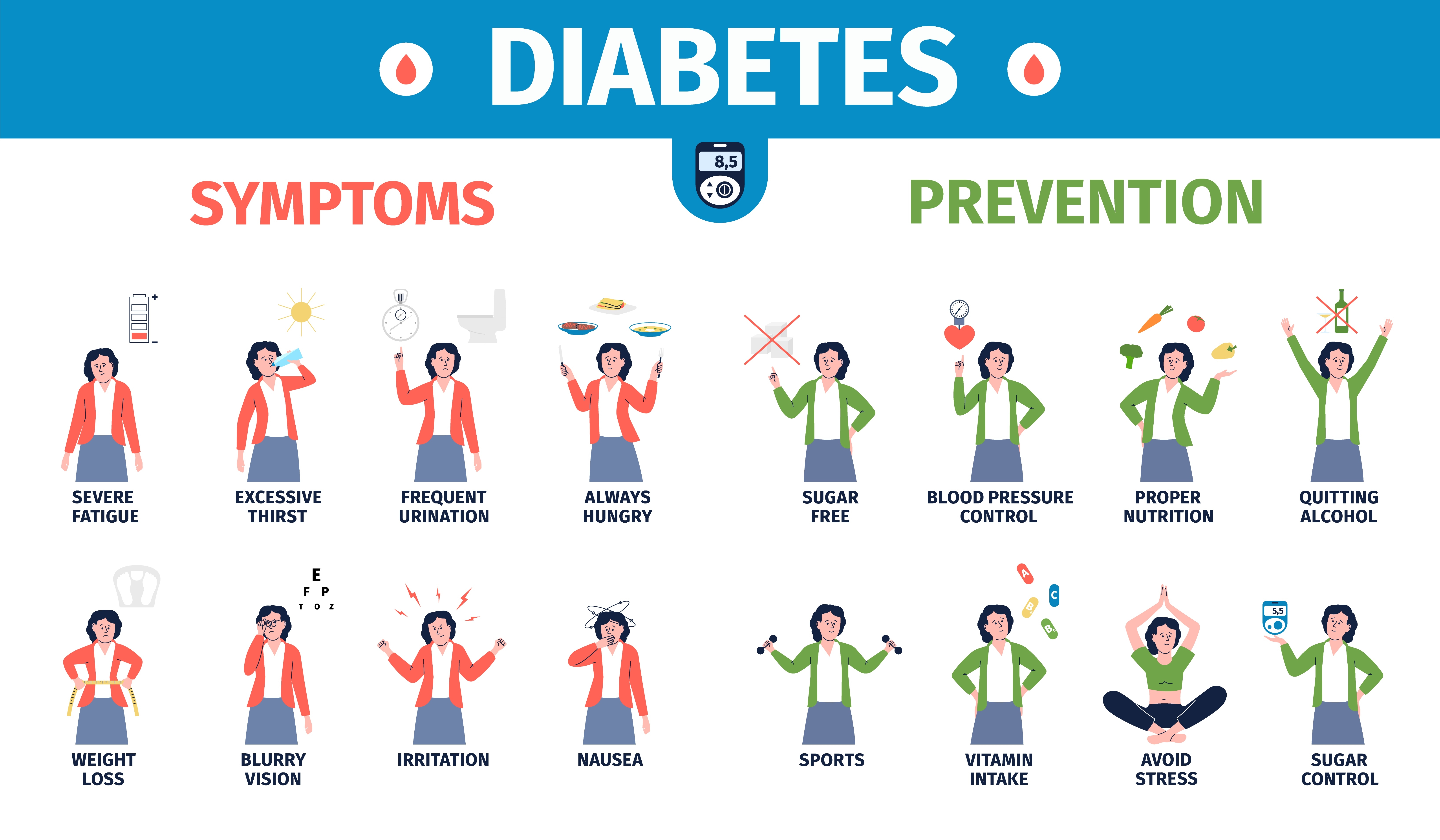
Normal Blood Sugar Levels 正常な血糖値 |
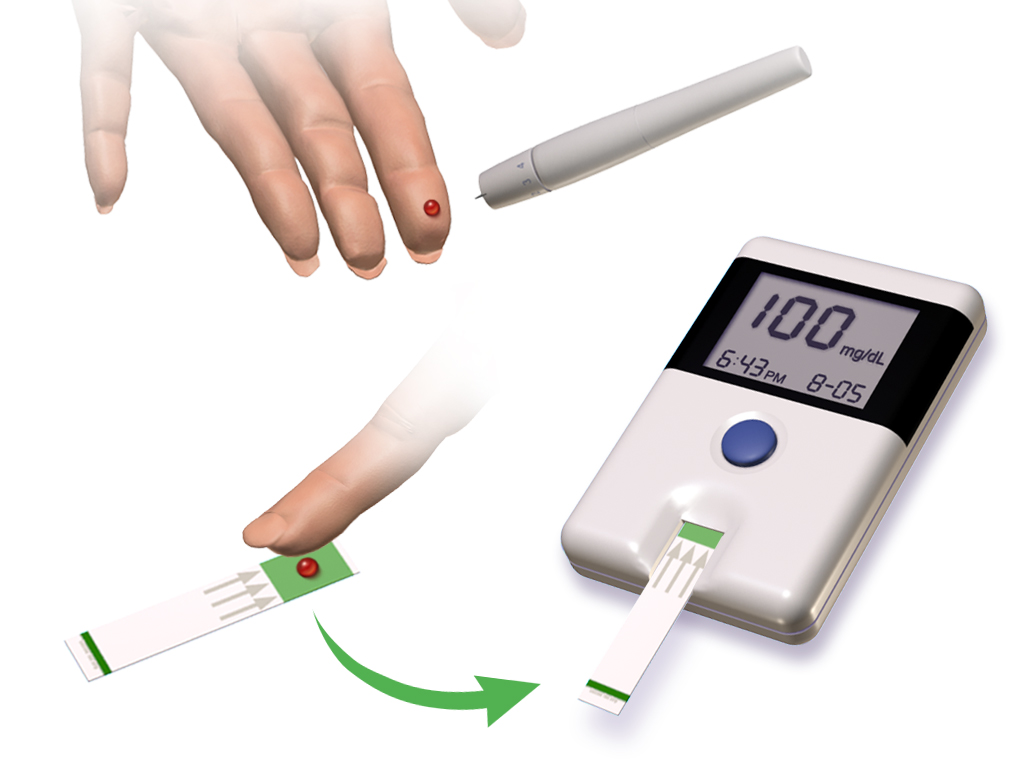
Normal Blood Sugar Levels are provided in the Blood Glucose Chart. A simple diabetes blood test using diabetes test strips allows for continuous blood glucose monitoring at home.
How do you check your blood glucose level?
Put blood from a finger prick on a diabetes test strip. Blot off excess blood with a tissue. Read the glucose test strip either by comparing the colour with the colour chart on the test strip bottle or by using an electronic blood glucose meter. It is important to follow the instructions on the bottle or meter carefully.
When should you check your diabetes blood sugar levels?
你应该什么时候检查你的糖尿病血糖水平?
Routinely
For Diabetes Mellitus type 2 (usually controlled by diet for diabetes and diabetes medicine, or by diet alone), 2-3 times each week at different times of the day is enough.
For Diabetes Mellitus type 1 (which requires insulin), more regular checking is required; that is, at least once a day, usually first thing before breakfast and then about 2 hours after a meal.
Your blood glucose levels are likely to be low before meals and high 2 hours after meals.
Special Circumstances
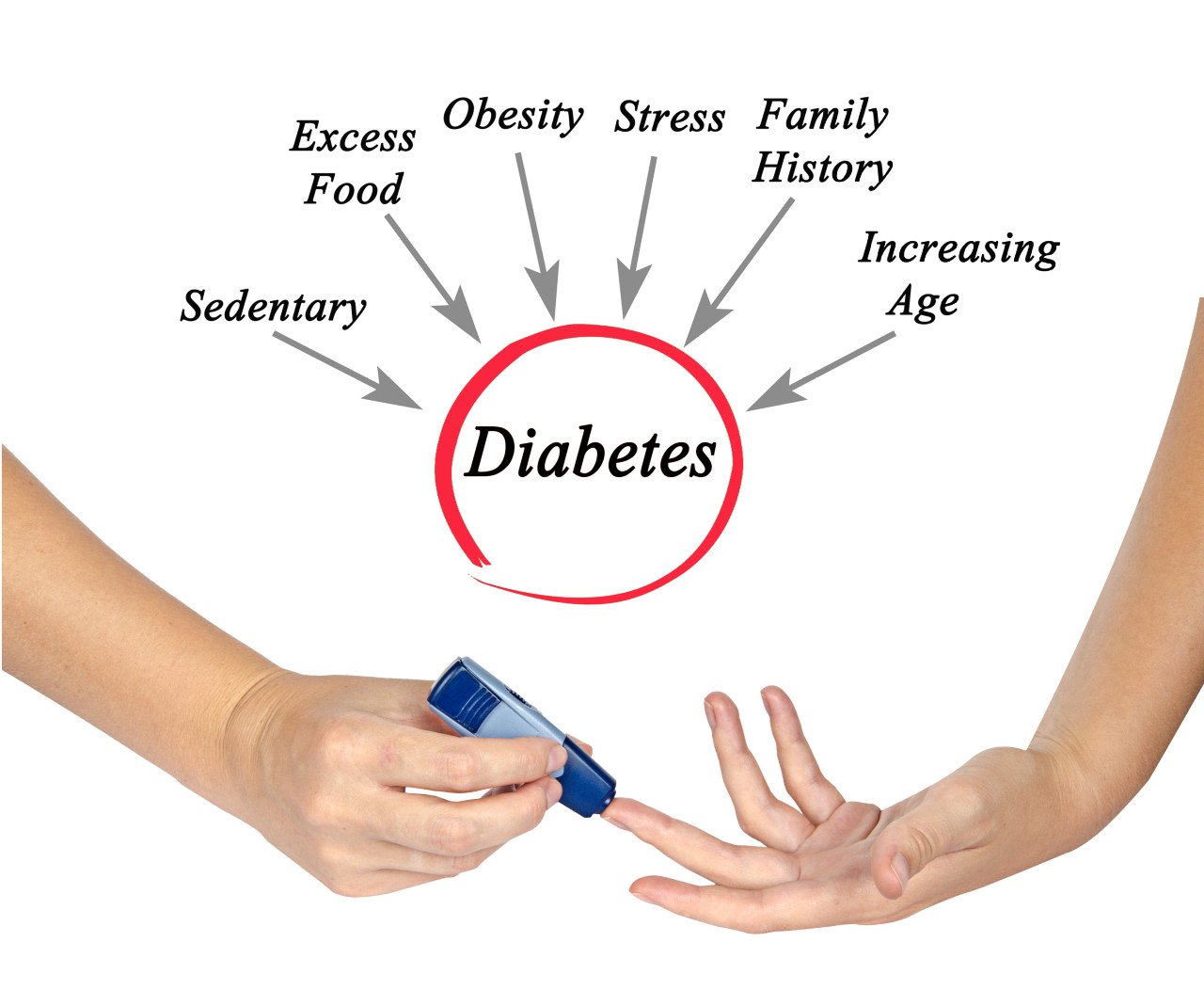
Stress, illness or too much food will push your blood glucose level up and you can get high blood sugar readings.
Exercise and your diabetes medications will pull your blood glucose level down.
When you are ill or under a lot of stress or exercising more than usual, you may need to check your blood sugar levels more often than usual.
What are the Ideal Blood glucose levels?
理想的血糖水平是多少?
Ideal or normal blood sugar levels are 3-6 mmol/L before meals and 3-7 mmol/L 2 hours after meals.
Fair control is a blood sugar level range of 6-8 mmol/L before meals and 7-10 mmol/L after meals.
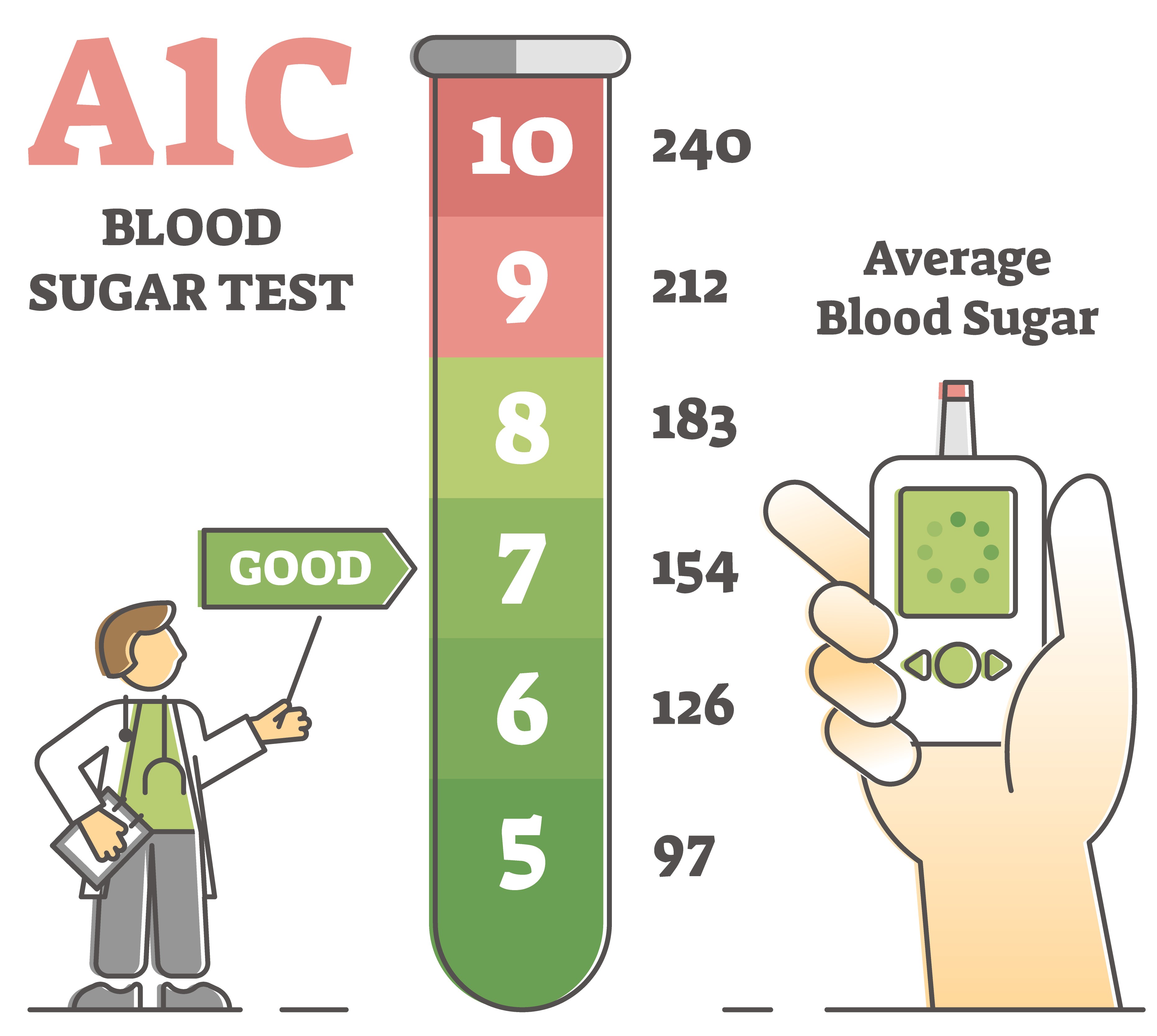
- Normal Blood Sugar Range (Targets of Glycaemic Control)
|
|
HbA (%)
Pre-meal Glucose mmol/L (mg/dL)
2-hour post-meal glucose mmol/L (mg/dL) |
|
- Diabetes Blood Sugar Levels that are sub-optimal or unacceptable
|
|
HbA (%)
Pre-meal Glucose mmol/L (mg/dL)
2-hour post-meal glucose mmol/L (mg/dL) |
|
* Based on Singapore Ministry of Health Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus 2006
Diabetes Self Management by Continuous glucose monitoring
通过持续血糖监测进行糖尿病自我管理
- Check your blood glucose level regularly, and record the result and the date and time of the test in a blood glucose log.
- Be careful to follow the instructions accurately.
- Ideal or normal blood sugar range is between 3 and 7 mmol/L.
- If you are ill or under stress, your blood glucose level is likely to go up. You should check it more often than usual, and see your doctor if it does go up.
Don't forget to record the date, time and result of your blood sugar test.
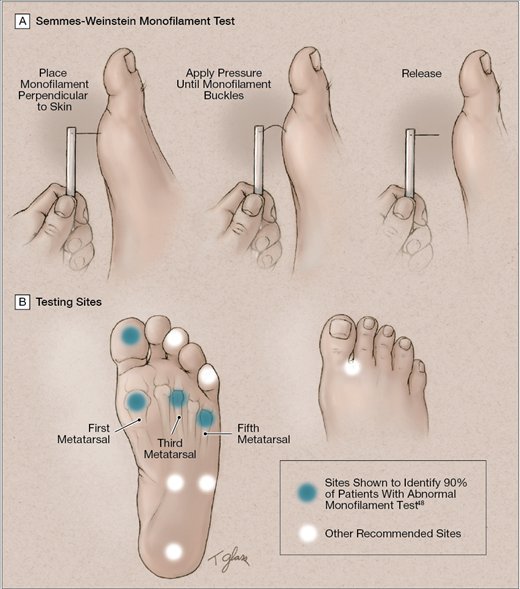
Diabetic Neuropathy Easy Self Assessment
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerves throughout your body. Diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in your legs and feet.
You may use a piece of stiff fishing line string to do this easy Diabetic foot self test. If you have lost sensation in any of the spots indicated in the above diagram, seek medical advice from your family doctor to get a professional diagnosis and medical intervention.
'An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.'
Health Assessment & Screening Packages
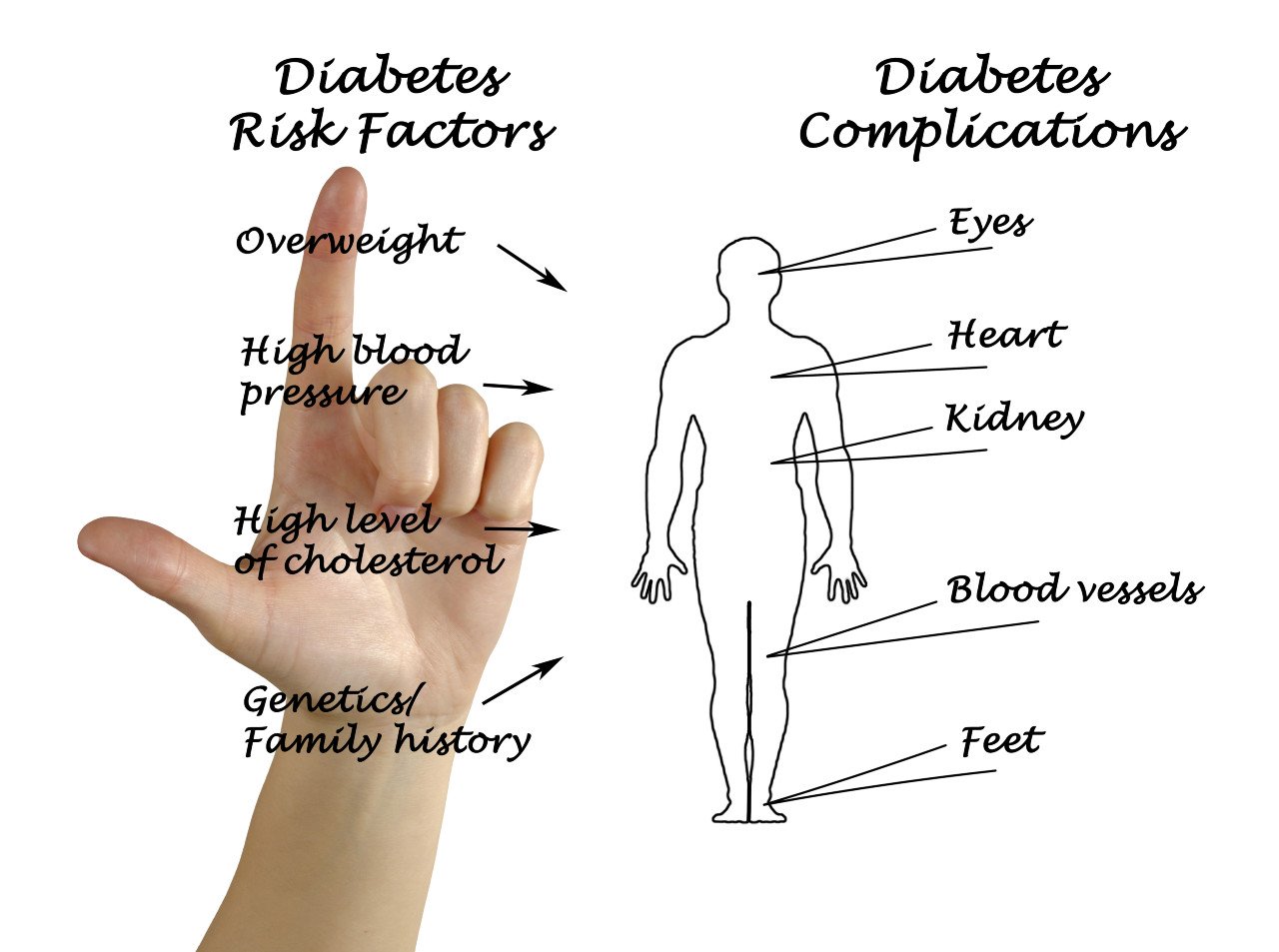
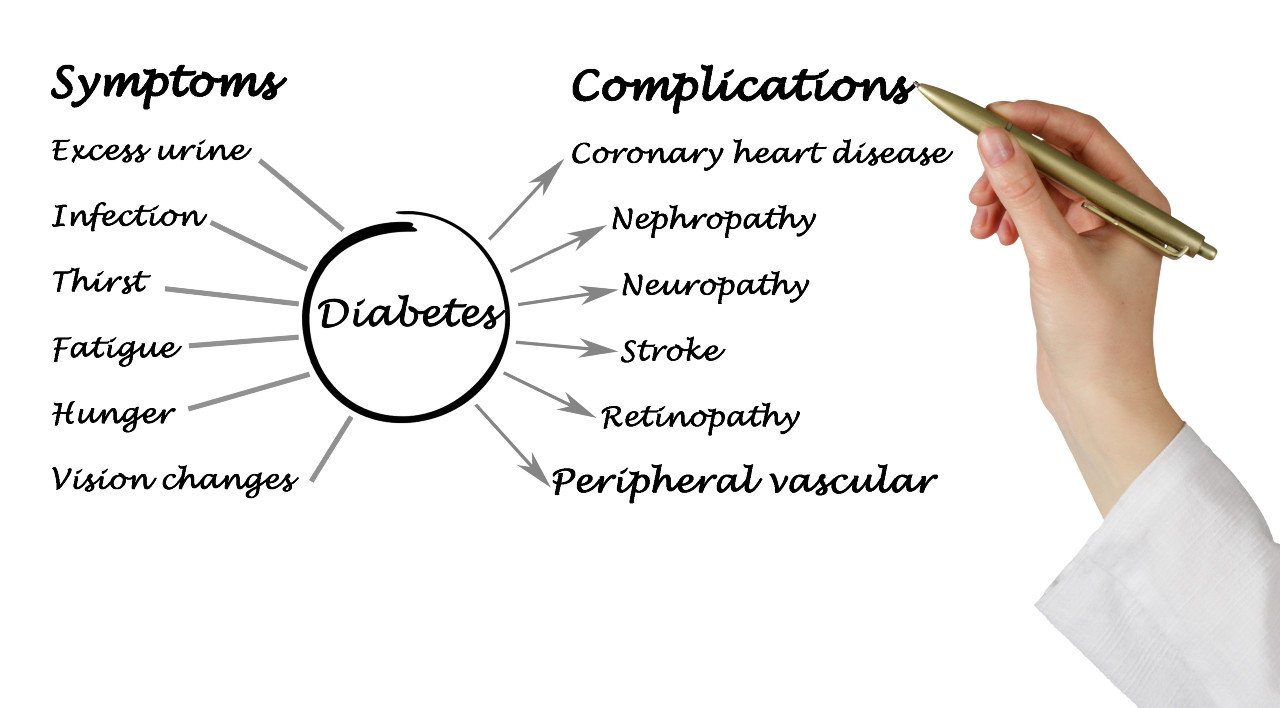
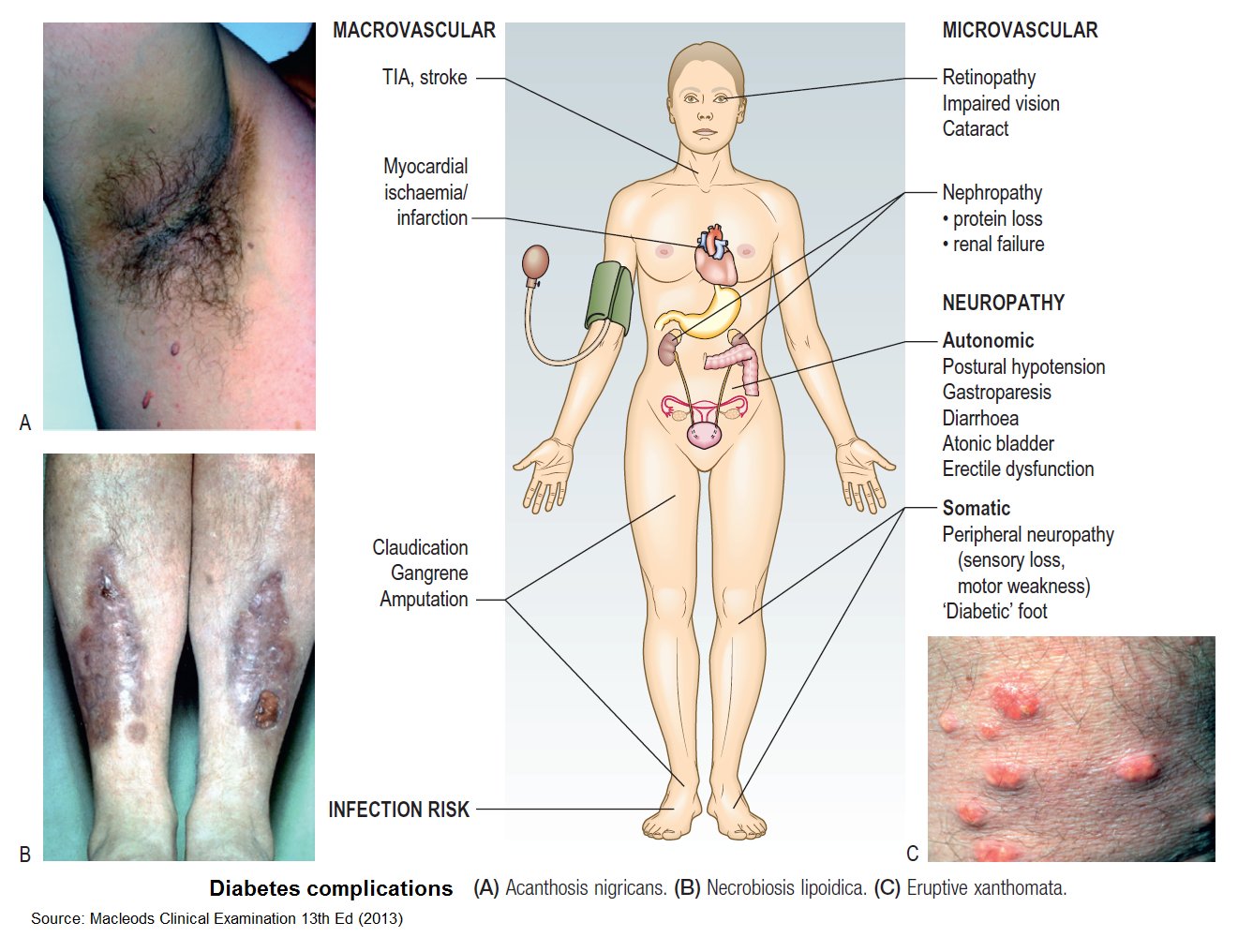
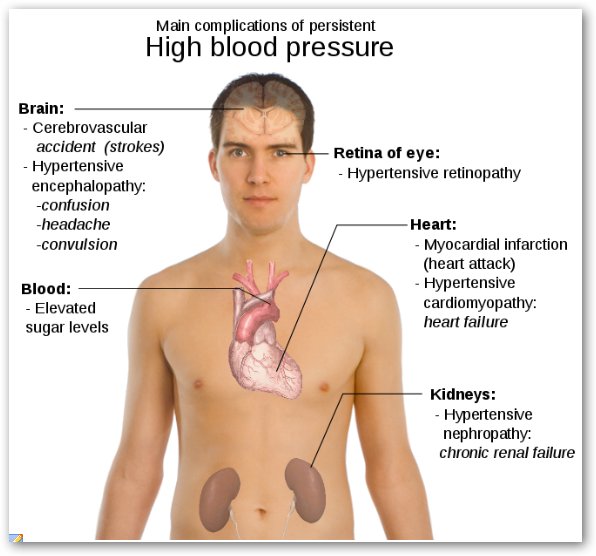
Complications of Diabetes
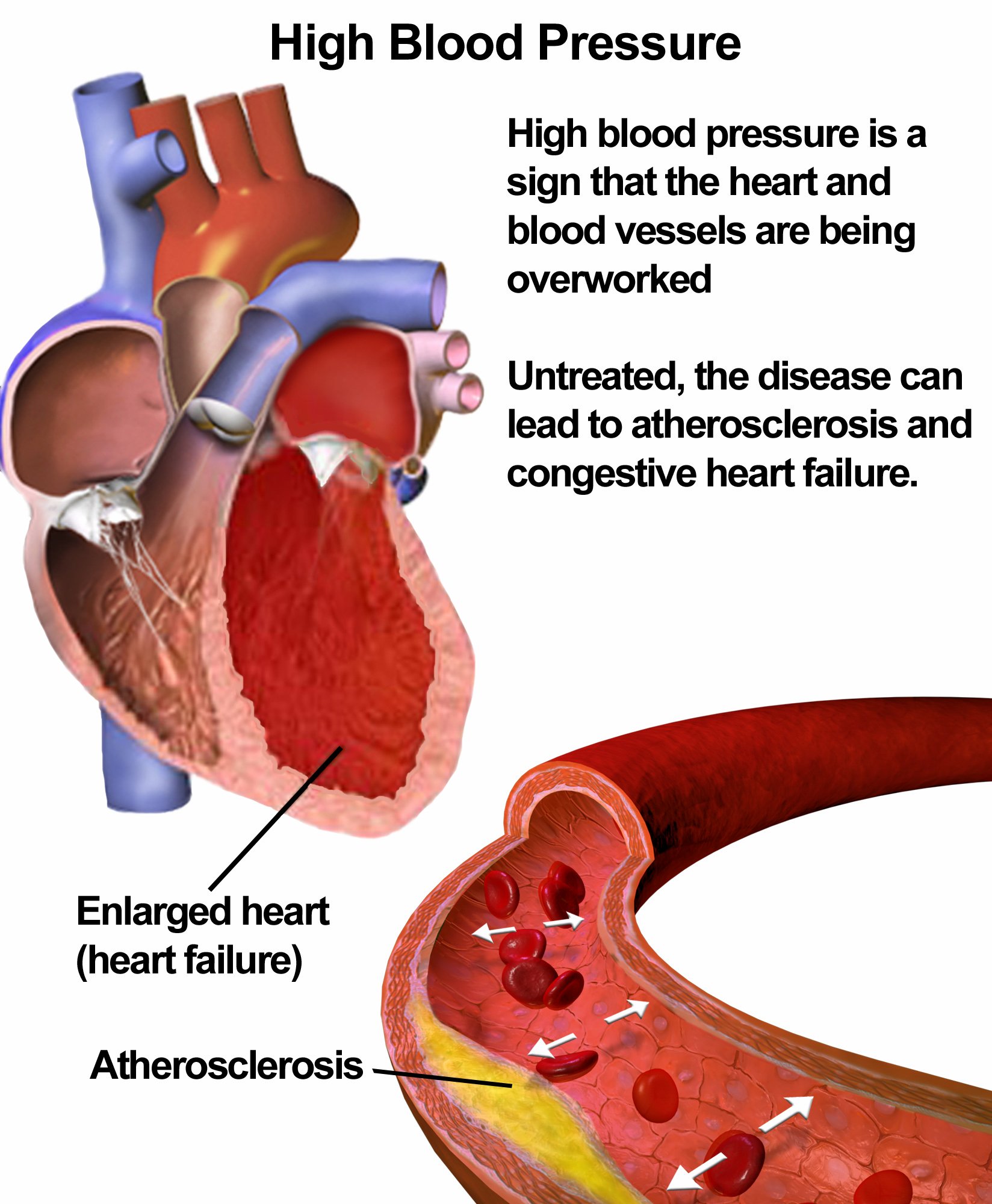
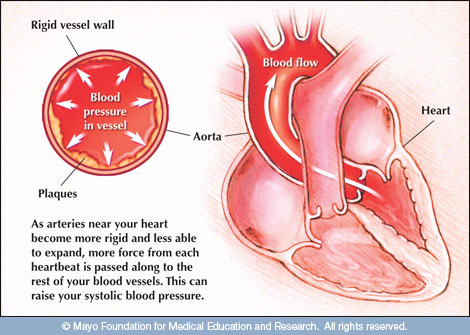
Hypertension Symptoms & Treatment, Blood Pressure monitoring, BP Chart
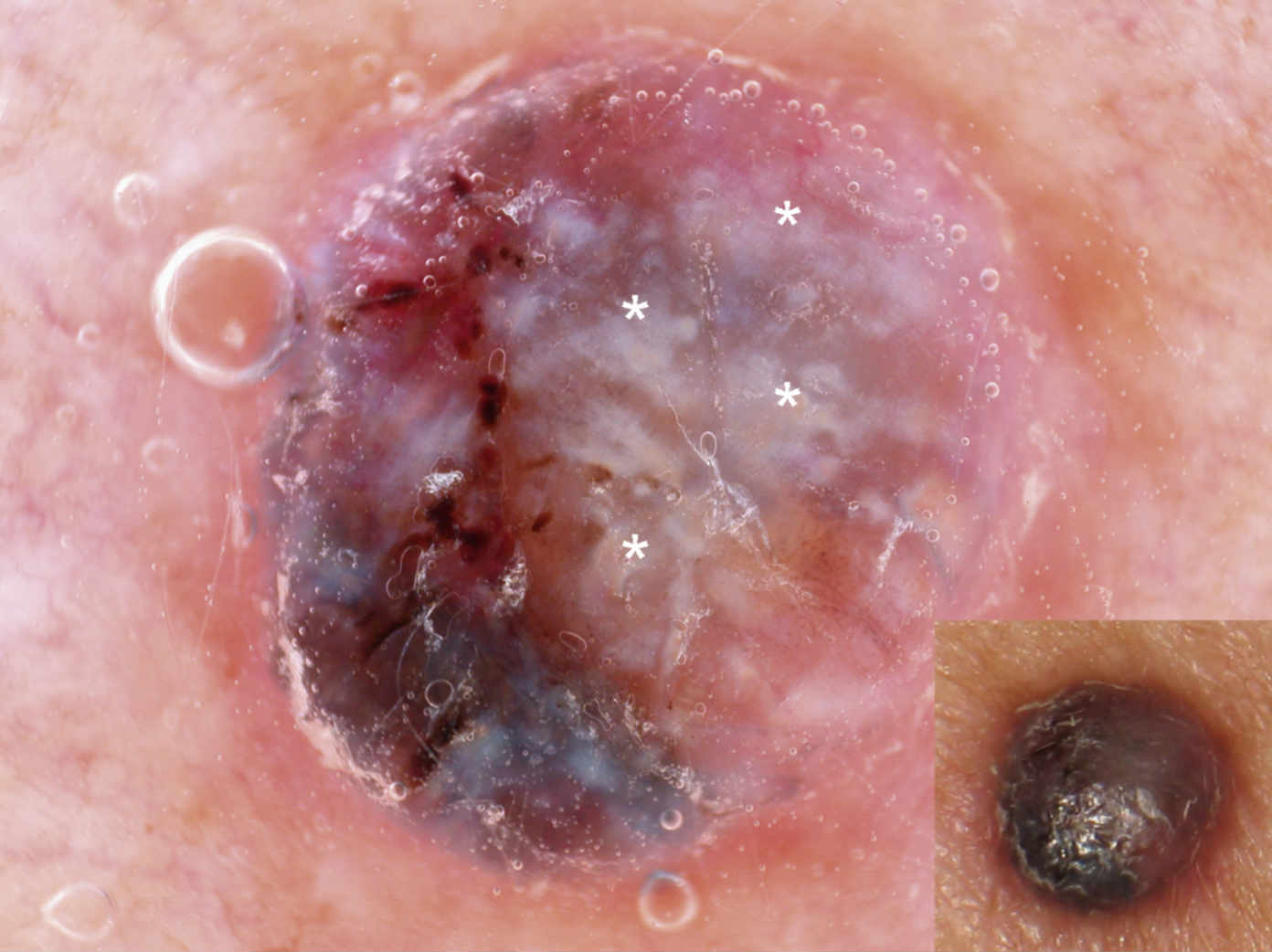
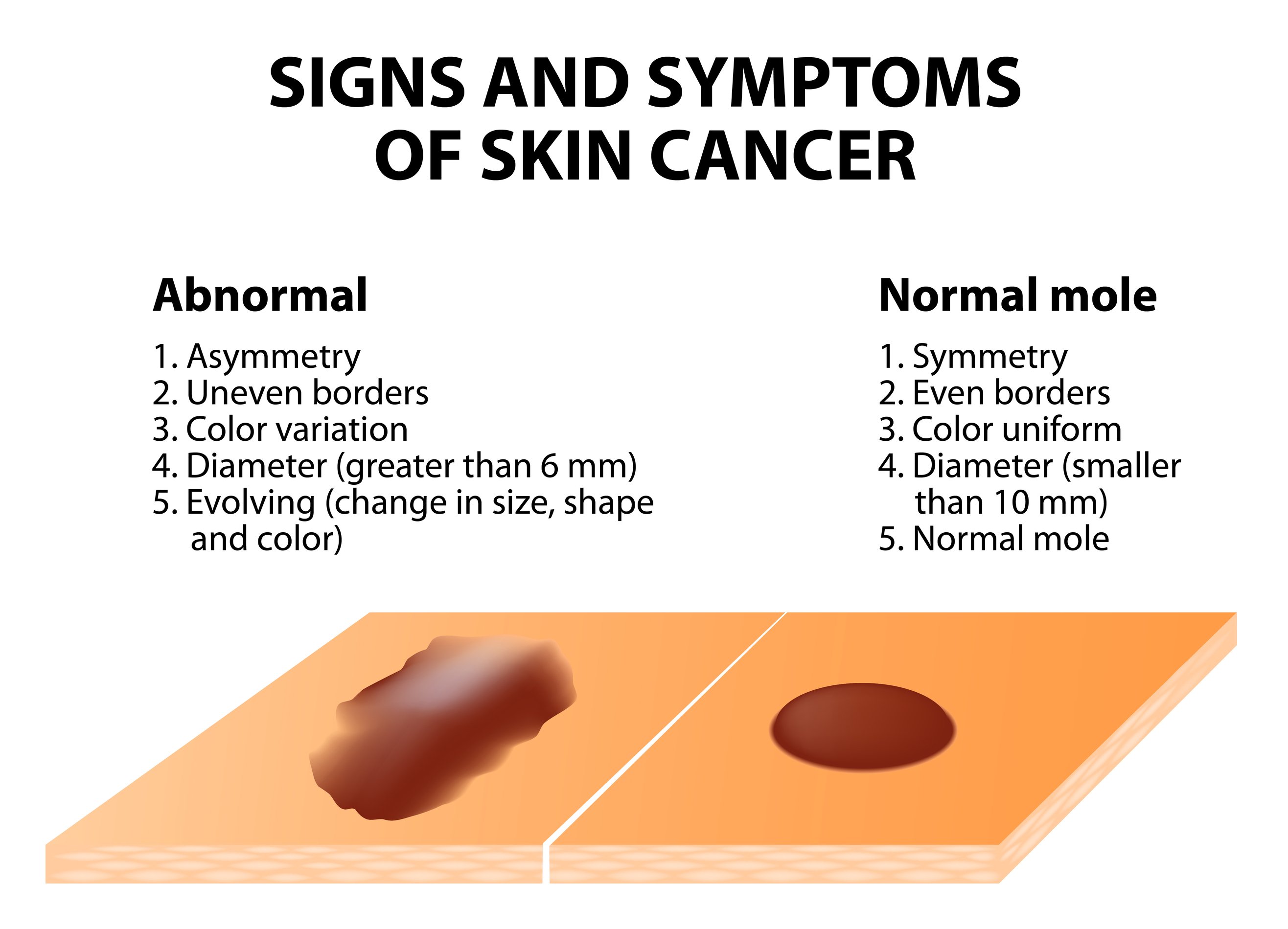
Learn what is Cancer, Skin Cancer-Types, Causes & Prevention, Melanomas Explained & Detecting Skin Cancer with Dermoscopy.
The information provided in this website is for knowledge purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice.
Should you encounter any medical problem that you are unsure of, always consult your doctor or health care provider for assistance and medical advice.