|
Latest Influenza Vaccines (Protects against Flu and H1N1 Viruses) Make your Appointment at Tel: 6694 1661 |
COVID-19 Sinopharm Vaccine & Booster
Sinopharm COVID-19 Vaccine is currently Out Of Stock at our clinic.
Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV vaccine has now been approved for use by private clinics in Singapore against the COVID-19 virus under the Special Access Route. It is the first China-made vaccine to be approved by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
To date, more than a billion doses of the Sinopharm BBIBP-CorV have been administered. The vaccine has also been approved for use in over 50 countries around the world.
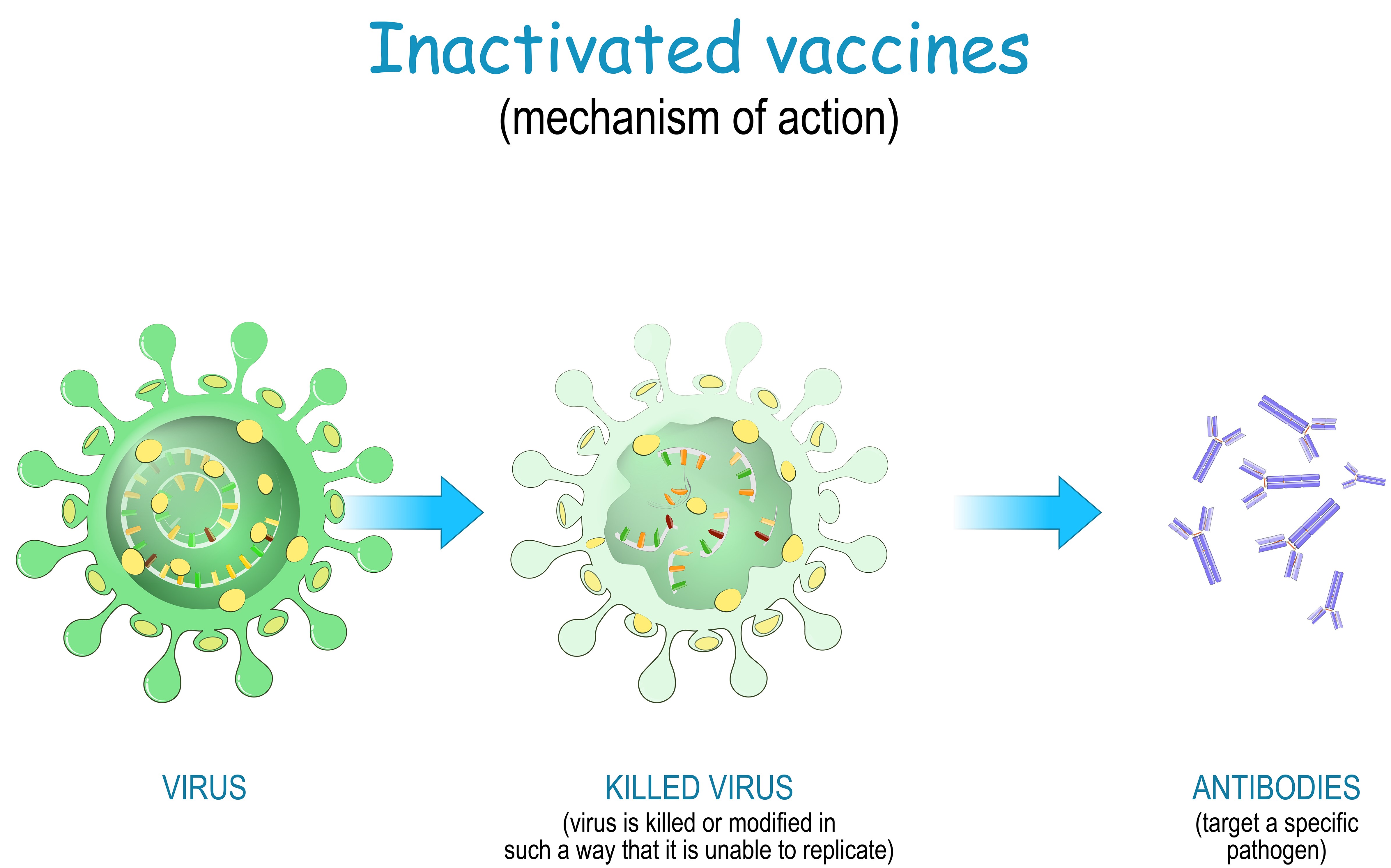
Inactivated vaccines are a tried-and-tested form of vaccine technology which is used in other well-established vaccines, such as the Flu and Hepatitis B vaccines.
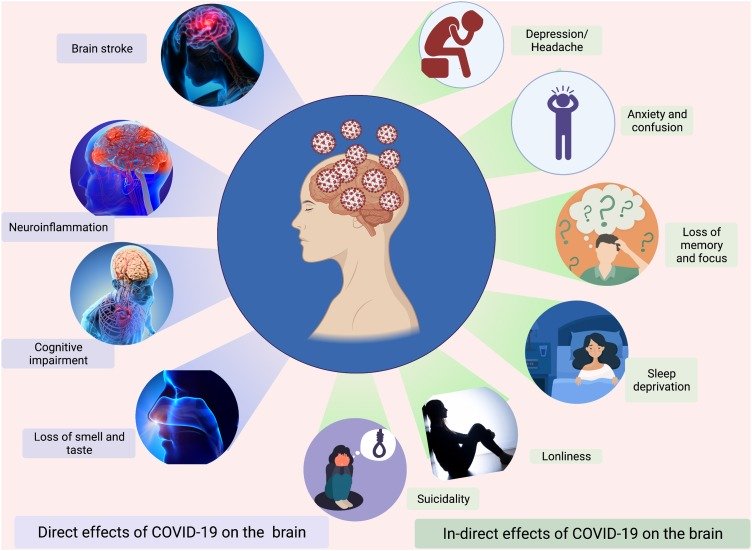
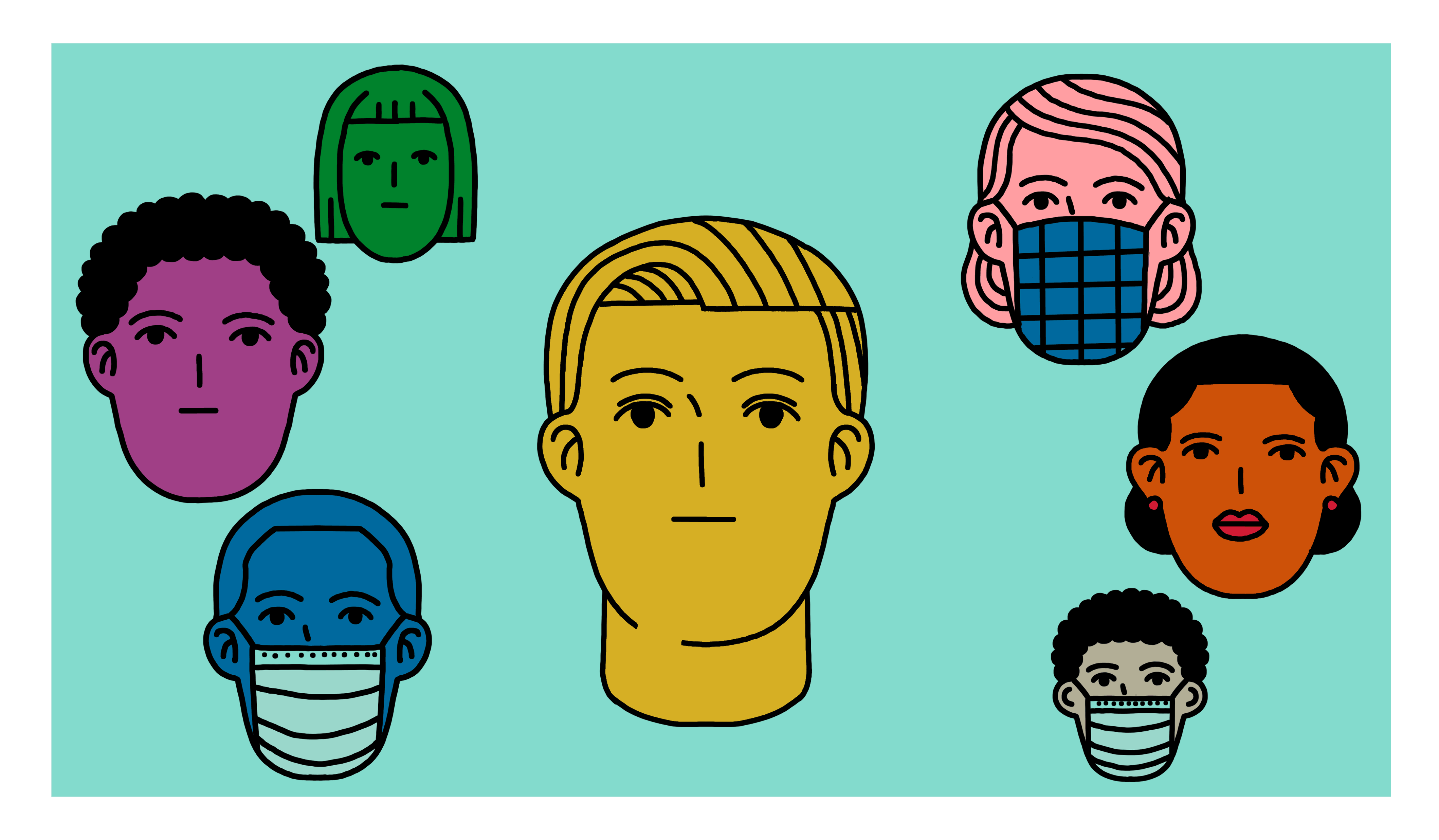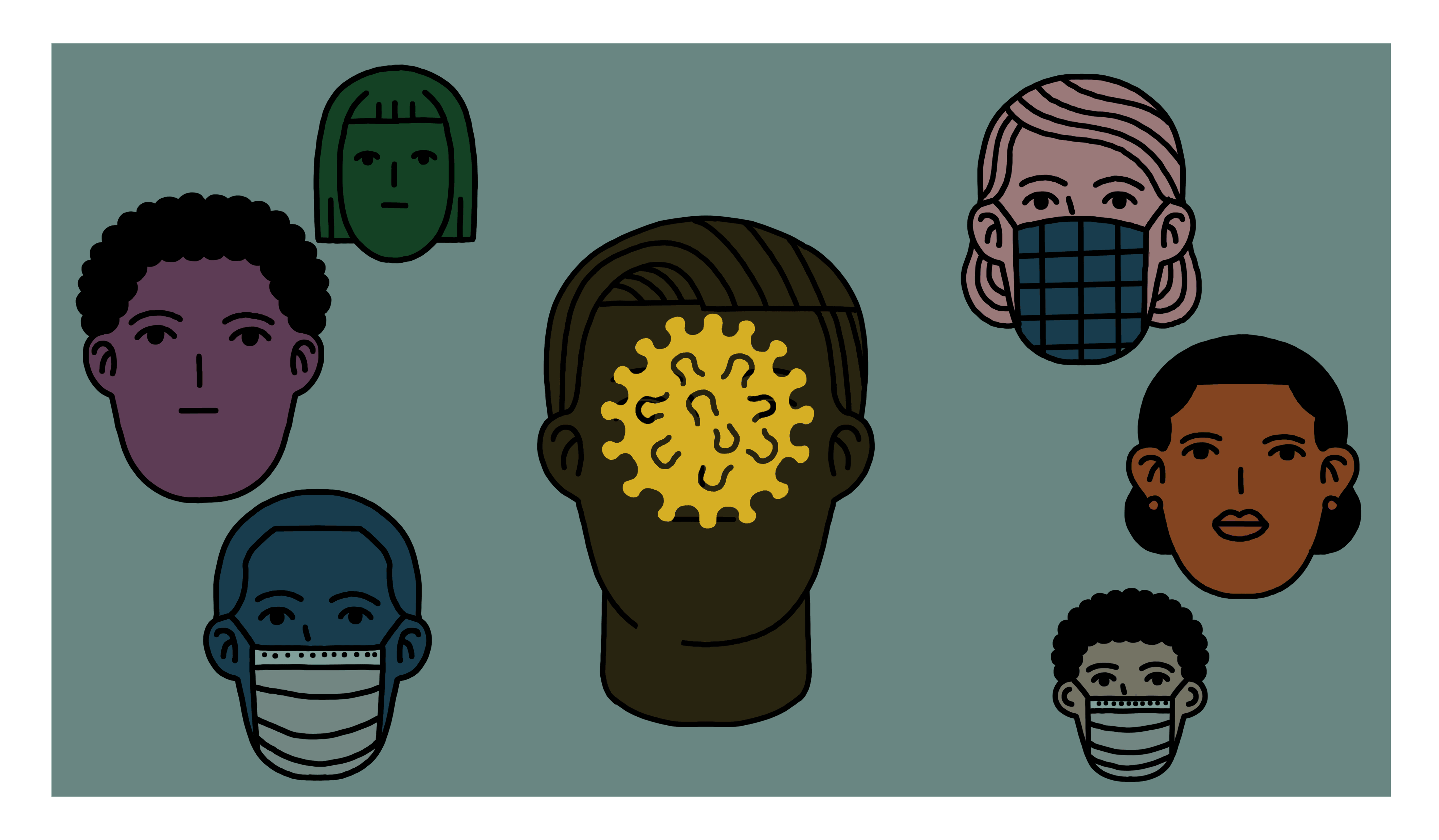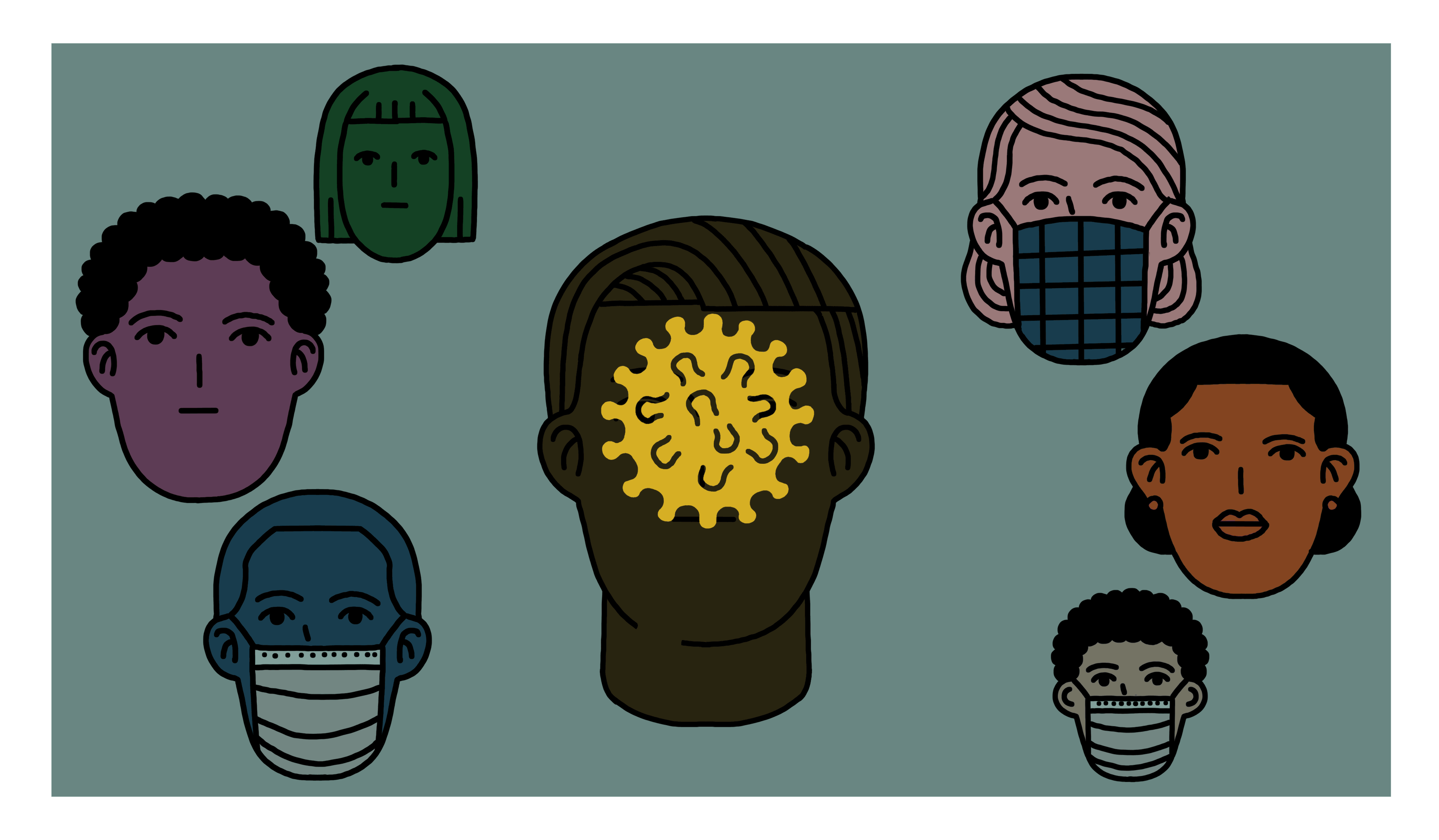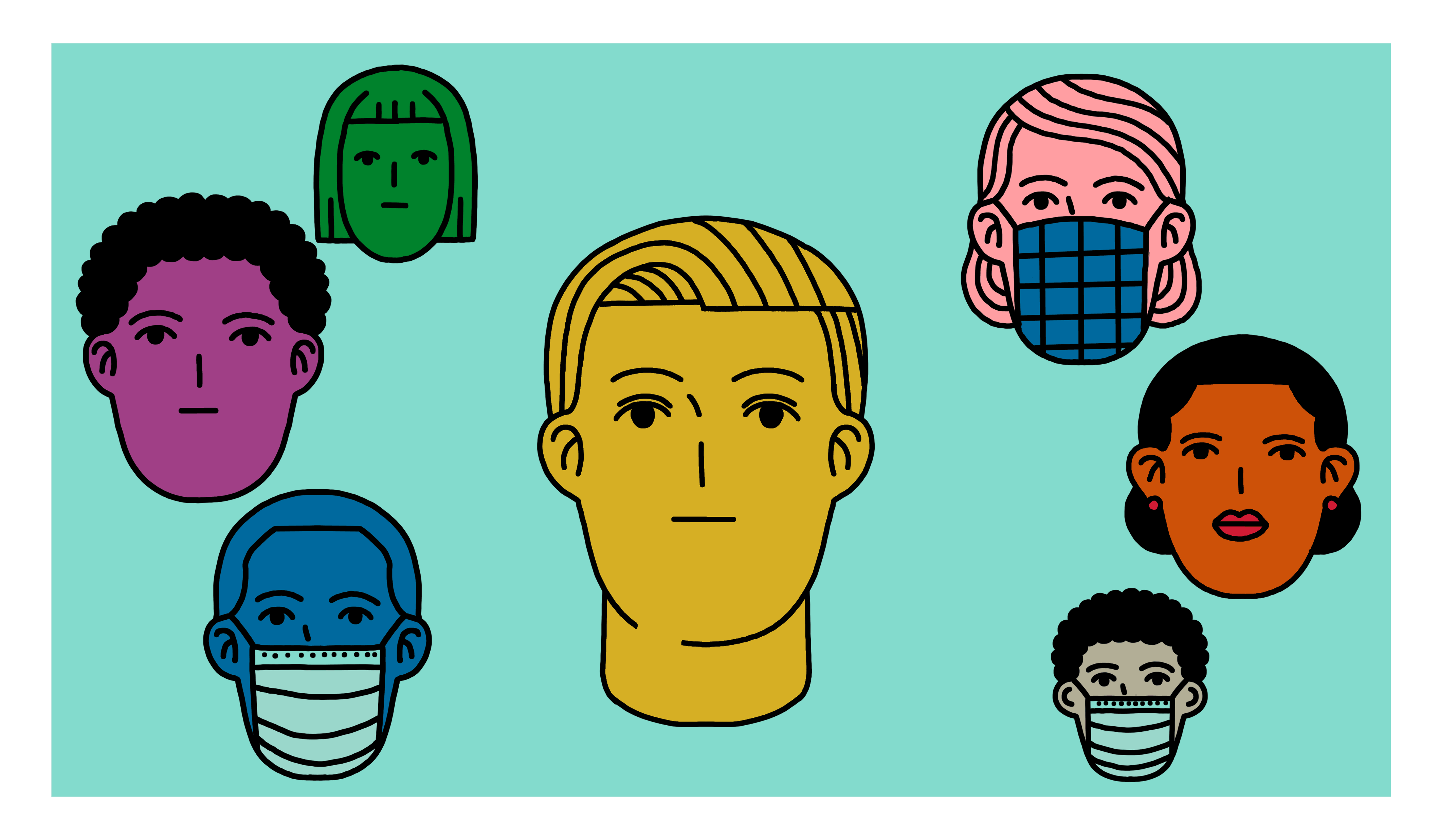
Effects of COVID-19 on the Brain
|
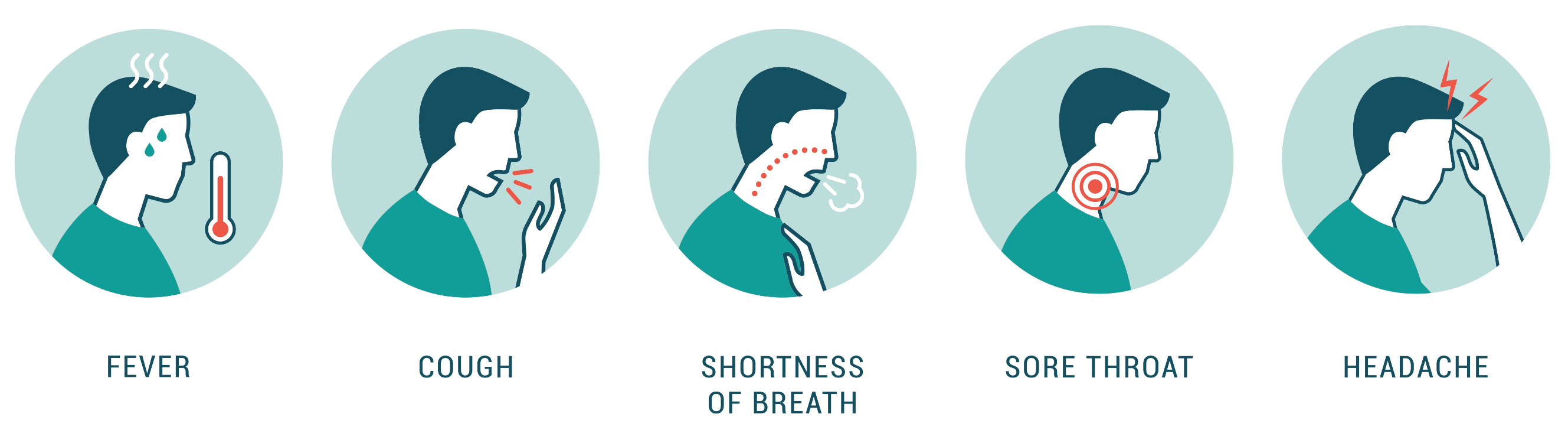
COVID Symptoms to watch out for: |
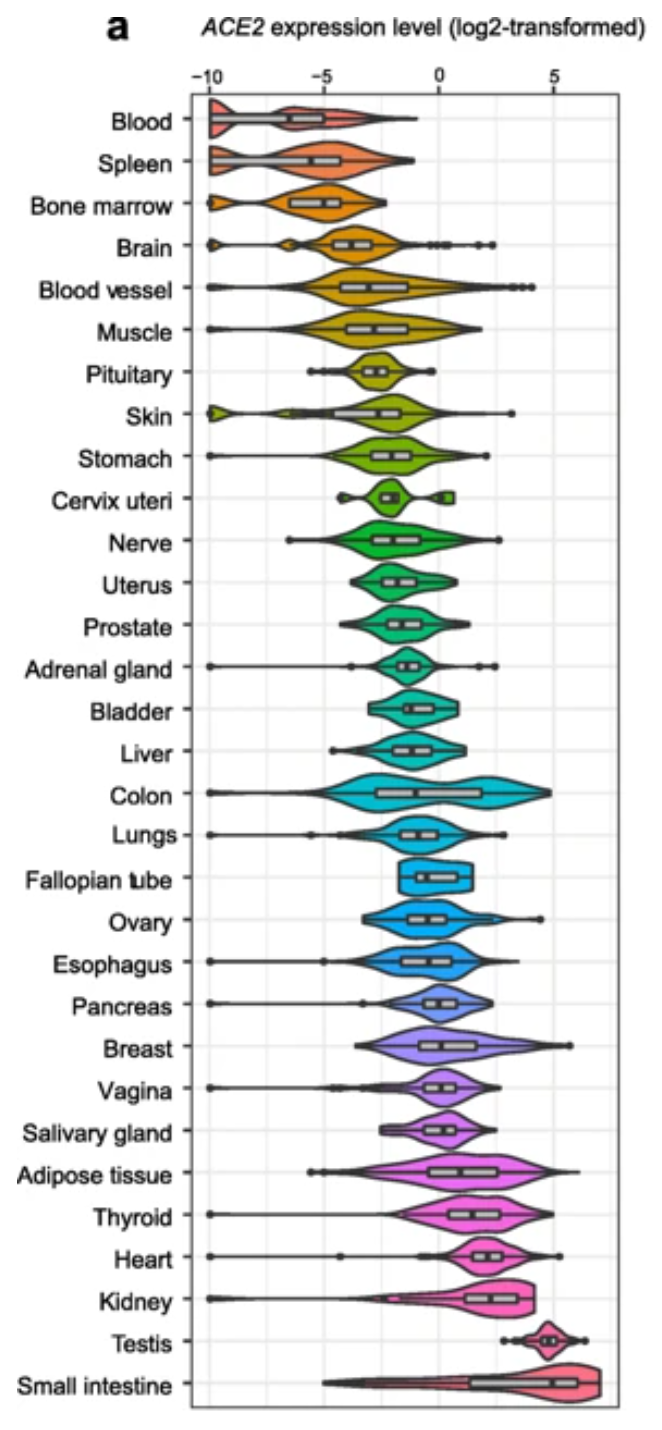
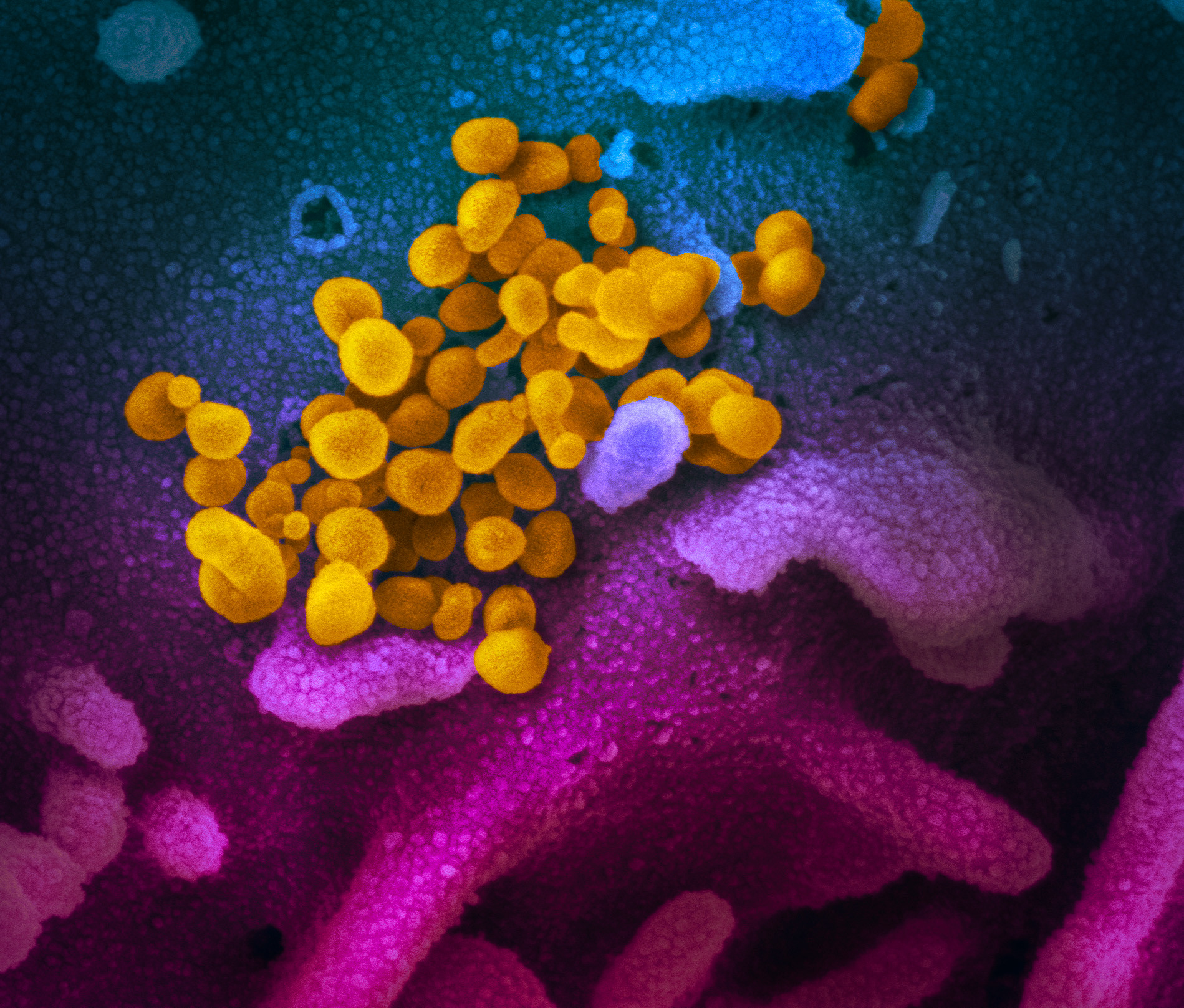
SARS-CoV-2 Virus Infection of Human Organ Tissues through Cell ACE-2 Receptors: |
Singapore Ministry of Health Recommendation:
- For persons who have already completed their Primary series with mRNA vaccines and are recommended to get a booster, but are unable to take another dose of mRNA vaccines for medical reasons, they may boost using one dose of Sinopharm vaccine. The booster should be taken six months after mRNA dose 2 (M-M-S).
- For persons who are unable to take the 2nd dose of mRNA vaccines for medical reasons, they may complete their vaccination with the Sinopharm vaccine. 2 doses of the Sinopharm vaccine is recommended to complete the Primary series. The 2nd Sinopharm dose should be taken 28 days after the 1st Sinopharm dose (M-S-S).
For recovered persons who had not completed a primary series before infection:
- For persons who have recovered from a COVID-19 infection but received 1 dose or none of COVID-19 vaccination prior, they may receive 2 doses of the Sinopharm vaccine (28 days interval between doses), 3 months after the date of infection to complete a primary vaccination series (Recovered-S-S or S-Recovered-S-S or M-Recovered-S-S).
- For persons who have recovered from a COVID-19 infection and had received 2 doses of Sinovac or Sinopharm vaccines prior, they may receive 1 dose of Sinopharm after 3 months from the date of infection to complete a primary vaccination series (S-S-Recovered-S).
Potential Discovery To Get Rid Of Spike Protein
Dr. Tina Peers discusses a potential new discovery in eliminating spike protein and reducing long-haul symptoms. Other compounds have been studied like Quercetin, Bromelain, NAC and Nattokinase to name a few. Please do your own research on these supplements.
- COVID Vaccine & Booster - Sinopharm vaccine
- Flu Vaccine
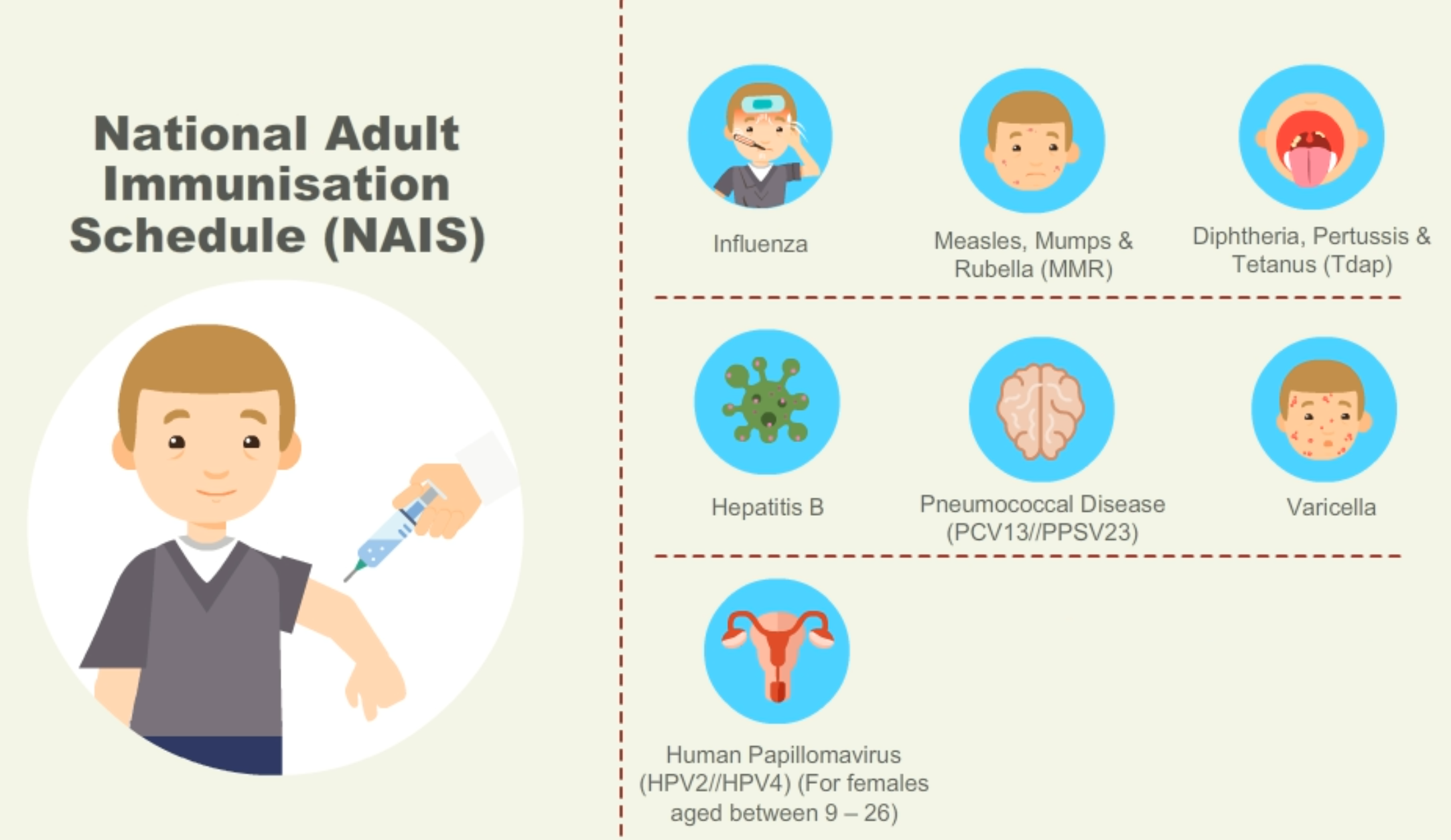
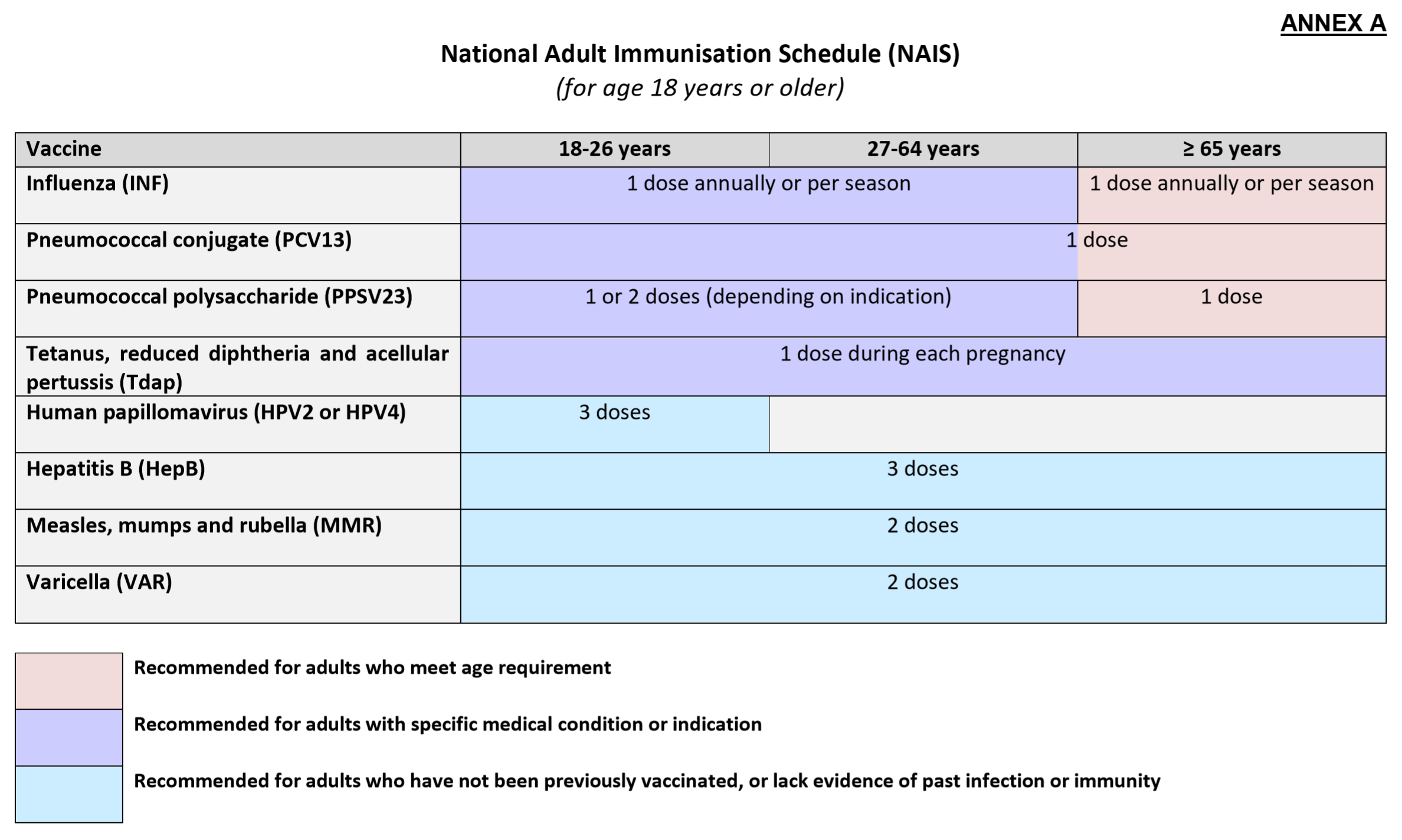
- Childhood & Adult Vaccine schedule (Refer to NAIS & NCIS)
Up to $400 per Medisave Account per year can be used for Vaccinations under the National Adult & Childhood Immunisation Schedule
- Influenza, Pneumococcal (PCV13/PPSV), Human Papillomavirus
(HPV2/HPV4), Hepatitis B, Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis (Tdap),
Measles, Mumps & Rubella (MMR) and Chickenpox (Varicella)
June 2020 Update
Sinovac Biotech has entered Phase 3 clinical trials for its coronavirus vaccine. The vaccine has safely elicited an immune response from Phase 2 human trials. The Beijing-based company’s vaccine, called CoronaVac, has not caused severe side effects and more than 90% of people administered with the shot on a 14-day interval have induced neutralizing antibodies two weeks after inoculation.
Using a killed version of the coronavirus, Sinovac’s vaccine is among five Chinese experimental COVID-19 vaccines that have reached the crucial final stage of human testing before they can be approved for public use. The vaccine is now being tested in Brazil, a current COVID hotspot where the novel pathogen has caused the second-largest outbreak in a global pandemic that so far infected more than 7.7 million people and killed over 428,000.
Some of the world’s leading vaccine efforts are seeking to conduct phase III trial in active outbreaks to evaluate the effectiveness of their shots. The vaccine co-developed by the University of Oxford and AstraZeneca Plc are also undergoing late stage trials in Brazil, while Cambridge, Massachusetts-based Moderna Inc. is set to go into phase III trials in the US.
- Oxford COVID-19 vaccine to begin phase II/III human trials. Working with AstraZeneca, they hope to start production of the vaccine which comes in the form of an inhaler by August 2020.
- Three COVID-19 vaccines are undergoing phase II clinical trials in China. China also recently approved clinical trials for two types of inactivated vaccines for COVID-19 in Apr 20. Chinese scientists have been racing to develop COVID-19 vaccines via five approaches – inactivated vaccines, genetic engineering subunit vaccines, adenovirus vector vaccines, nucleic acid vaccines, and vaccines using attenuated influenza virus as vectors. (Ref: The Lancet - Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of a recombinant adenovirus type-5 vectored COVID-19 vaccine: a dose-escalation, open-label, non-randomised, first-in-human trial)
- GSK (GlaxoSmithKline) and Sanofi, two of the world’s biggest vaccine manufacturers are collaborating to develop an adjuvanted COVID-19 vaccine, using Sanofi’s recombinant DNA technology. They are starting phase I clinical trials in the second half of 2020 and anticipate mass producing the vaccine by the second half of 2021.
Vaccine Adjuvant
A vaccine adjuvant is an ingredient of a vaccine that helps promote a better immune response, when administered in conjunction with an antigen, creating a stronger and longer lasting immunity against infections than the vaccine alone. Adjuvants also can reduce the amount of virus needed for production of a vaccine, which can allow for greater supplies of vaccine to be manufactured.
COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 Virus Information
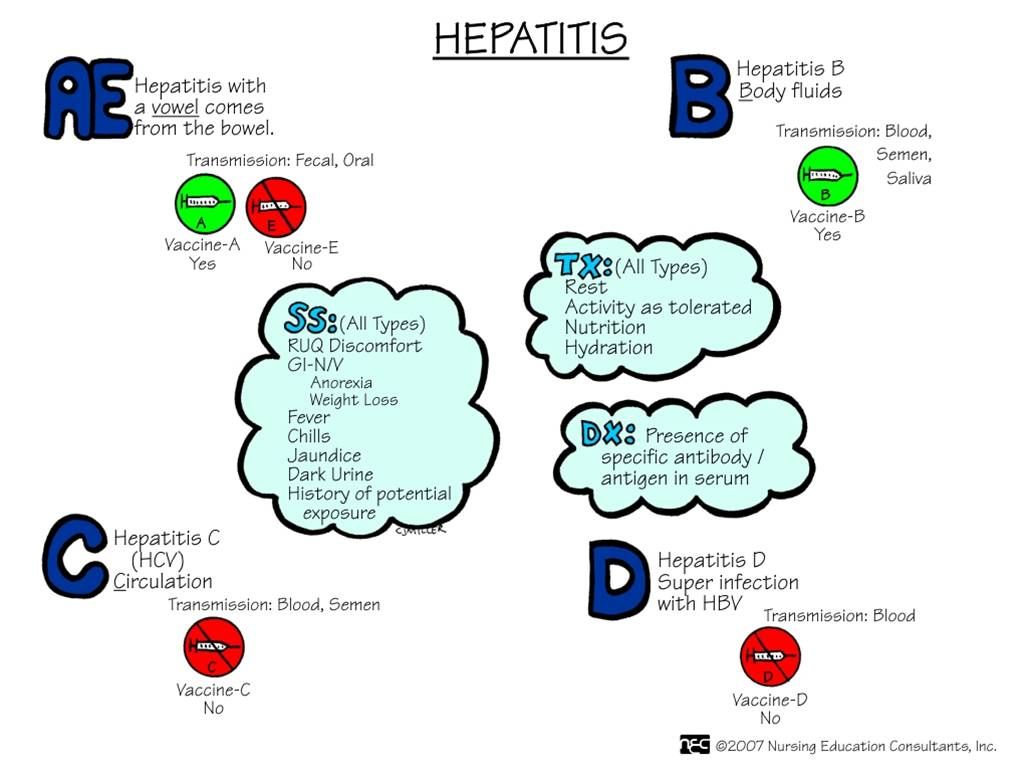
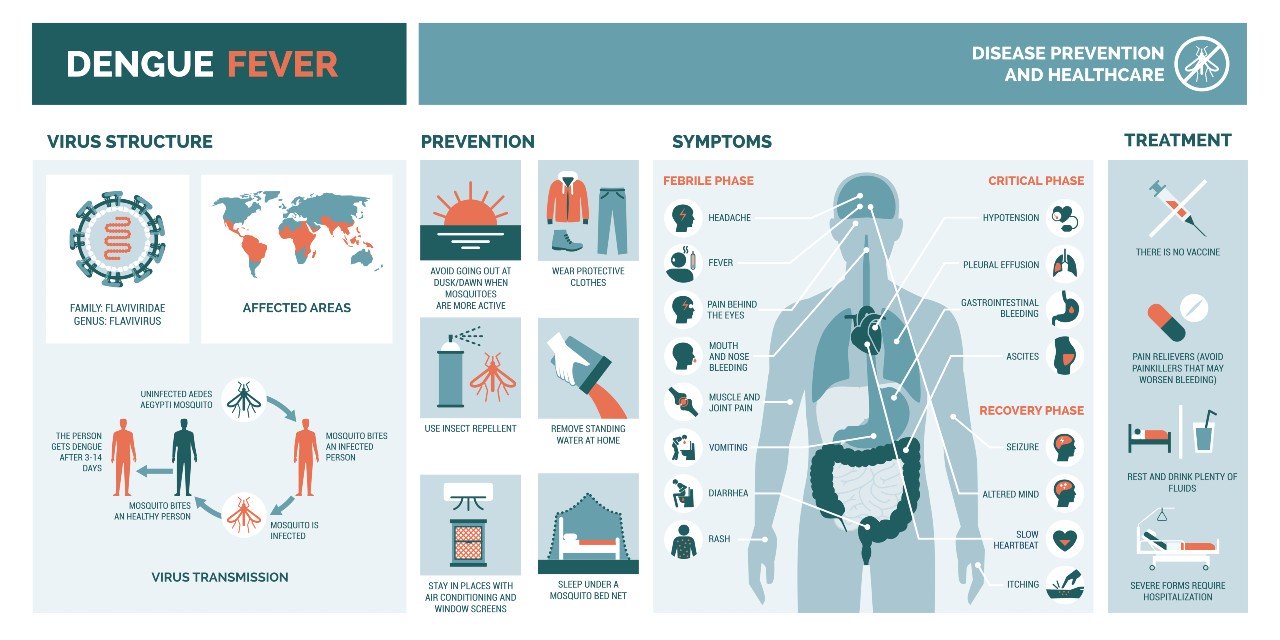
Infectious Diseases - Dengue Fever, Influenza, Hepatitis B, COVID-19
Vaccines come in several different types :
Inactivated - Some vaccines contain inactivated, but previously virulent, micro-organisms that have been destroyed with chemicals, heat, or radiation eg polio vaccine
Attenuated - Some vaccines contain live, attenuated micro-organisms. Many of these are active viruses that have been cultivated under conditions that disable their virulent properties, or that use closely related but less dangerous organisms to produce a broad immune response. Although most attenuated vaccines are viral, some are bacterial in nature eg viral vaccines for measles, mumps and rubella and the bacterial disease typhoid.
Toxoid - vaccines are made from inactivated toxic compounds that cause illness rather than the micro-organism eg tetanus and diphtheria. Toxoid vaccines are known for their efficacy.
Protein subunit - rather than introducing an inactivated or attenuated micro-organism to an immune system, a fragment of it can create an immune response eg the subunit vaccine against Hepatitis B virus that is composed of only the surface proteins of the virus, produced by recombination of the viral genes into yeast; or the virus-like particle (VLP) vaccine against human papillomavirus (HPV) that is composed of the viral major capsid protein, and the sununits of the influenza virus. Subunit vaccine is being used for plague immunization.
Conjugate - Certain bacteria have polysaccharide outer coats that are poorly immunogenic. By linking these outer coats to proteins (e.g toxins), the immune system can be led to recognize the polysaccharide as if it were a protein antigen. This approach is used in the Influenza type B vaccine.
Heterotypic - These are vaccines that are pathogens of other animals that either do not cause disease or cause mild disease in the organism being treated. The classic example is the use of cowpox to protect against smallpox. A current example is the use of BCG vaccine made from Mycobacterium bovis to protect against human tuberculosis.
Experimental Vaccines
1. Recombinant vector – by combining the physiology of one micro-organism and the DNA of another, immunity can be created against diseases that have complex infection processes eg vaccine that was used to combat Ebola virus in Congo.
2. RNA vaccine - A novel type of vaccine which is composed of the nucleic acid RNA, packaged within a vector such as lipid nanoparticles. A number of RNA vaccines are under development to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
Valence
Vaccines may be monovalent (also called univalent) or multivalent (also called polyvalent). A monovalent vaccine is designed to immunize against a single antigen or single microorganism. A multivalent or polyvalent vaccine is designed to immunize against two or more strains of the same microorganism, or against two or more micro-organisms. In certain cases, a monovalent vaccine may be preferable for rapidly developing a strong immune response.
Healthy Aging 健康老龄化
Asymptomatic patients may display no symptoms of illness. Vulnerable people should get vaccinated against Influenza which protects susceptible people from, as well as exclude the Flu and H1N1 viruses should they start to show URTI or ARI symptoms.
a. Vaccination decreases the risk of co-infection with COVID-19.
b. Vaccination reduces the burden of respiratory illnesses in the healthcare system.
The latest Influenza Vaccine is now available. It protects against the Flu and H1N1 Viruses. Ministry of Health Safety protocols are adhered to at all times for the safe vaccination of you and your family.
* Importance of Keeping your
Vaccinations Up-to-date
Romina Libster: The power of herd immunity
How do vaccines prevent disease — even among people too young to get vaccinated? It's a concept called "herd immunity," and it relies on a critical mass of people getting their shots to break the chain of infection. Health researcher Romina Libster shows how herd immunity contained a deadly outbreak of H1N1 in her hometown. (In Spanish with subtitles.)
Are the Pneumococcal (PCV) & Influenza vaccines Protective against COVID-19?
Many COVID-19 infections which develop complications cause pneumonia and some are fatal, predominantly among older adults. Co-infection with other viruses or bacteria, particularly those that similarly cause inflammation of the respiratory tract would increase the risk for severe COVID-19 disease. Vaccinating older adults at higher risk of severe COVID-19 disease against vaccine-preventable diseases may help to reduce the strain on the healthcare system from those diseases during a pandemic and also alleviate some of the potential COVID-19 mortality due to co-infecting pathogens.
Vaccines that can prevent respiratory tract infections, particularly in older adults, either through direct protection or indirectly through high coverage childhood immunisation programmes, include vaccines against seasonal influenza, Streptococcus pneumoniae, measles, Bordetella pertussis and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib). Measles, pertussis and Hib vaccines are already included in almost all routine infant immunisation programmes globally and have largely eliminated the targeted pathogens as a risk to the older adult population through indirect protection.
Two vaccines that target a large burden of the respiratory disease in older adults are seasonal influenza vaccines and 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23). These vaccines are only included in routine adult immunisation in some countries (including Singapore) but with only moderate coverage.
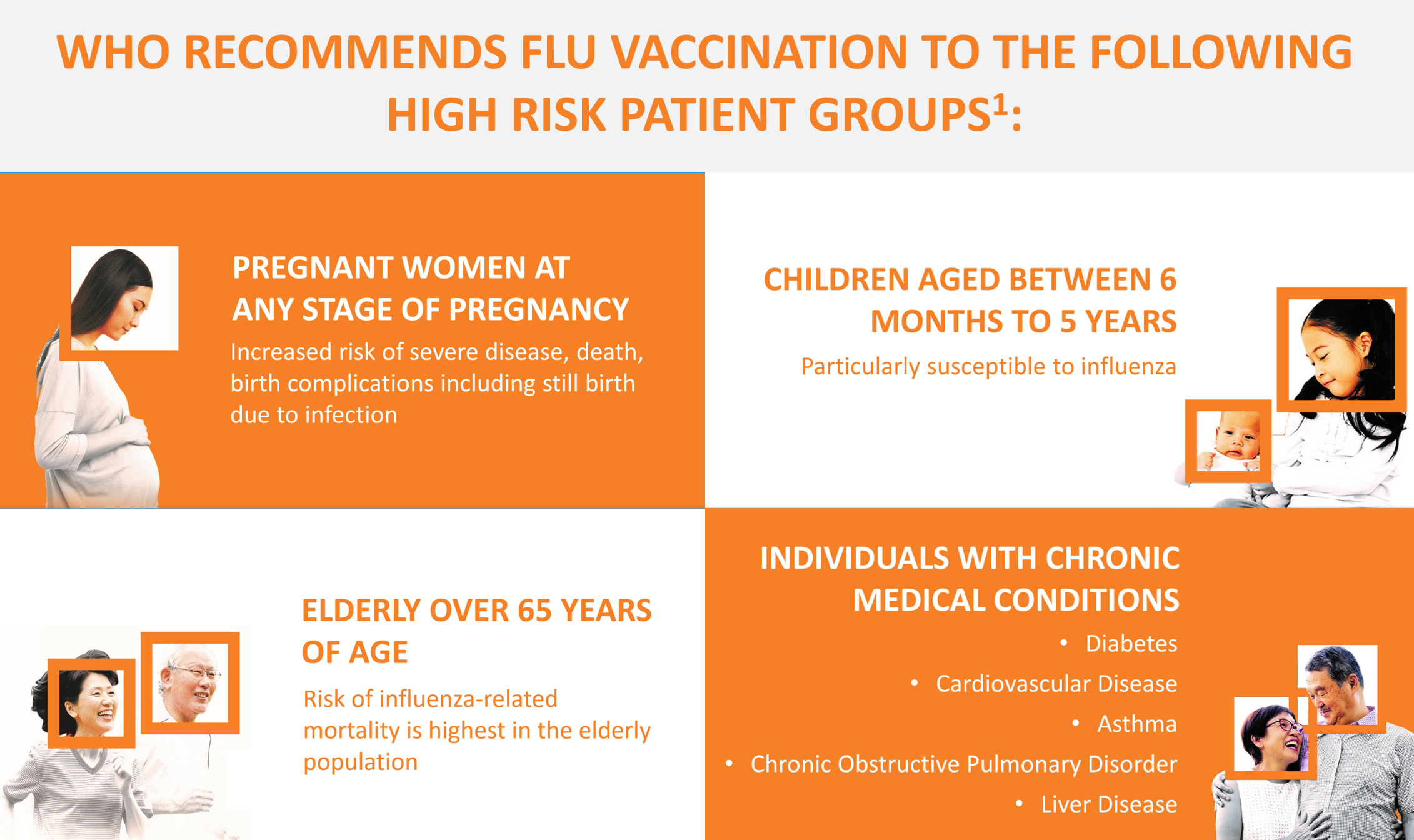
The World Health Organization recommends seasonal influenza vaccine use for pregnant women as well as older adults (>65yrs), healthcare workers and persons with specific chronic illnesses.
Influenza vaccination could prevent 20% to 60% of influenza infections and thereby potentially a similar percentage of influenza-attributable COVID-19 morbidity and mortality.
Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Vaccine
PPV23 targets 23 of the over 90 serotypes that are responsible for most adult pneumococcal disease. PPV23 is recommended for routine use in older adults in most high-income countries. PPV23 use in older adults could prevent up to 33-40% of pneumococcal disease and thereby potentially pneumococcal-attributable COVID-19 morbidity and mortality.
Pneumococci have been identified as a major source for often fatal secondary bacterial infections during pandemic and seasonal influenza infections. Estimates for the proportion of pneumococcal co-infections among pandemic influenza deaths range from about 7% during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic to more than 50% during the 1918 pandemic.
Are your Vaccinations Up-to-date?
Both seasonal influenza vaccine and PPV23 can prevent a substantial burden of targeted disease and mortality among older adults and adults at-risk. Despite a potential collateral reduction in influenza and pneumococcal circulation due to contact reducing interventions, in countries where the COVID-19 pandemic coincides with the season of high risk for pneumococcal and/or influenza disease, vaccination at high coverage will have added benefits: minimising the number of pneumococcal and influenza hospital admission reduces the resources needed to care for non-COVID-19 patients and minimises the risk of healthcare-acquired COVID-19 infections.
For influenza, the similarity of symptoms with COVID-19 cases also suggests that vaccination will increase the specificity of COVID-19 diagnosis and hence faster medical intervention.
Ref : https://cmmid.github.io/topics/covid19/covid19_siv_ppv23.html
Health Assessment & Screening Packages
Co-infection of COVID-19 with other infectious diseases is possible
Reduce your risk of getting sick with COVID-19
- Make
sure your vaccinations are up-to-date.
People older than 65 years, and those with many underlying conditions,
such as those who are immunocompromised or with significant liver disease,
are recommended to receive vaccinations against Influenza and
pneumococcal disease (PCV). Click here for Vaccination schedules (NAIS/NCIS).
- Do not delay getting medical care for your underlying condition because of COVID-19. MD International Medical Centre has contingency MOH infection prevention protocols to protect you from getting COVID-19 if you need care for your underlying condition.
- Continue your medications and do not change your treatment plan without talking to your doctor.
- Make sure that you have at least a two-week supply of your chronic disease medications.
- Call MDIMC @ Tel: 6694 1661 for a medical appointment if you have any concerns about your underlying medical conditions or if you get sick. Our clinic is a PHPC-accredited medical clinic. Under the MOH Swab & Go Home programme, our doctors can do a COVID-19 PCR Swab test if you meet the MOH medical crtieria.
NAIS & NCIS - Singapore is free from vaccine-preventable diseases like poliomyelitis, diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (whooping cough) because of our successful immunisation progamme.
National Adult Immunisation Schedule (NAIS) Singapore @ MD International Medical Centre. Make your vaccination appointment at Tel: 6694 1661.
Up to $400 per Medisave Account per year can be used for Vaccinations under the National Adult & Childhood Immunisation Schedule - Influenza, Pneumococcal (PCV13/PPSV), Human Papillomavirus (HPV2/HPV4), Hepatitis B, Tetanus, Diphtheria & Pertussis (Tdap), Measles, Mumps & Rubella (MMR) and Chickenpox (Varicella).
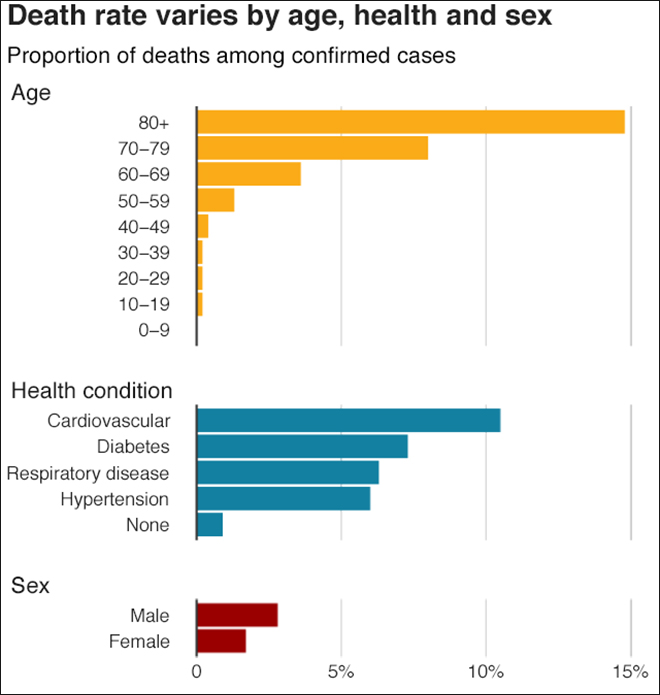
Groups at Higher Risk for Severe Illness in a COVID-19 Infection
Comorbidities & Underlying Health Conditions in COVID-19 Patients with Complications
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic lung diseases including COPD
- Chronic Kidney disease
- Asthma
- Dementia
- Chronic Neurological Disorders
- Cancer
- Rheumatological Disorder
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Chronic Hematologic disease / Haemoglobin Blood Disorders
- Liver disease / Hepatitis B Infection
- Malnutrition
- Immunodeficiency / Immunocompromised eg HIV AIDS
- People aged 65 and older
- 高血压
- 糖尿病
- 脑血管疾病
- 心血管疾病
- 慢性肺部疾病
- 慢性肾病
- 哮喘
- 失智
- 慢性神经系统疾病
- 癌症
- 风湿病
- 肥胖
- 抽烟
- 慢性血液系统疾病/血红蛋白血液疾病
- 肝病/乙型肝炎感染
- 营养不良
- 免疫缺陷/免疫功能低下,例如 HIV AIDS
- 65岁及以上的人
(Ref: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-020-0642-3.pdf, Dailymail.co.uk, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32320003/, Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with Covid-19 in China: A Nationwide Analysis https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/early/2020/03/17/13993003.00547-2020
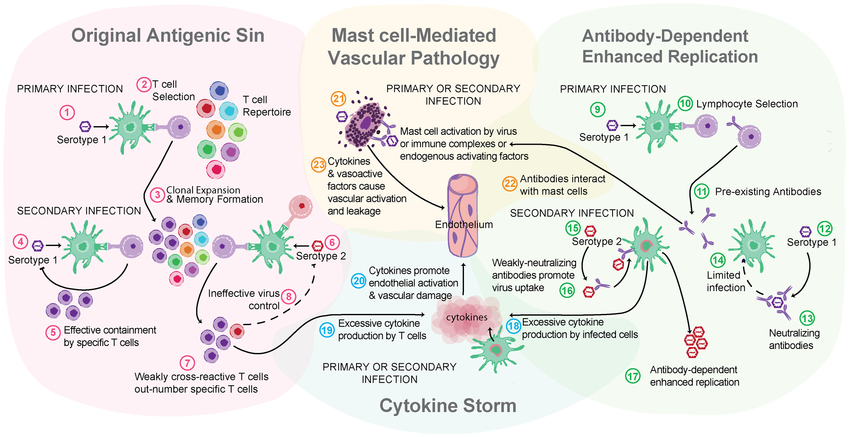
Immune-mediated Cytokine Storm plays a role in Severe COVID-19 Infections
- Cytokine Storms may occur in Infectious Diseases (eg SARS, Dengue etc) and lead to health complications, negative medical outcomes and/or mortality.
This is a severe immune reaction in which the body releases too many cytokines into the blood too quickly. Cytokines play an important role in normal immune responses, but having a large amount of them released in the body all at once can be harmful. A cytokine storm can occur as a result of an infection, autoimmune condition, or other disease. It may also occur after treatment with some types of immunotherapy. Signs and symptoms include high fever, inflammation (redness and swelling), and severe fatigue and nausea. Sometimes, a cytokine storm may be severe or life threatening and lead to multiple organ failure.
Pain Relief Management & Treatment, Vaccinations, Health Screening, COVID & Allergy Testing, Dermatology Treatments, Minor Surgical Procedures
MD International Medical Centre
Medical Services available:
- General Practice Family Medicine - Illnesses & Infections
- Minor Surgical Procedures
- IV Infusion of Medications
- Respiratory Medicine - Influenza, Colds, Cough, Upper Respiratory Tract Infections (URTI), Acute Respiratory Infections (ARI), Sinus Infection
- Treatment of Gastric issues, Stomach aches, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Heartburn
- Infectious diseases & Virology - COVID-19, Dengue, Flu, Hepatitis B etc
- Dermatology - Skin Problems (Eczema, Acne, Rash, Boils, Dermatitis, Pigmented or Dry Skin, Moles /Skin Tags /Wart Removal)
- Dermoscopy - Non-invasive Detection of Skin Cancer, Pubic lice & Scabies
- Treatment of Insect Bites & Stings
- Look Younger - Botox injections
- Eye Health / Ophthalmology - Conjunctivitis, Foreign body in the Eye etc
- Respiratory Medicine - Cough, Wheezing, Shortness of breath
- Ear, Nose & Throat (ENT) - Ear Wax Removal, Ear Otitis Enterna, Nose Bleed-Epistaxis, Snoring & Sleep Apnoea, Vertigo & Dizziness, Audiogram (Hearing test)
- Pain Management, Treatment & Therapy - Arthritis, Back & Joint Pain, Migraine, Gout
- Sports Medicine - Treatment of Sports Injuries
- Vaccinations / Immunization - Latest Flu vaccine, Sinopharm COVID Vaccine & Booster
- Travel Health - Travel Vaccinations & Health checks, Travellers' Diarrhoea
- Allergy tests / Allergic Rhinitis / Asthma Management
- Health Screening / Blood tests
- Management of Chronic Diseases - Treating Prediabetes, Diabetes & Insulin Resistance / Hypertension
- Heart Health - ECG Heart monitoring / High Cholesterol management / Chest pains
- Executive Health Assessment - Pre-Employment check-up / Work Permit / Employment Pass / Employment Pass
- Student Pass / Driving License Check-up
- Personal Health Management - Preventative Medicine & Disease Prevention
- Elderly / Senior Health
- Men's Health - Erectile Dysfunction medications etc
- Women's Health- Osteoporosis, Heavy Periods, Breast lumps, Urinary Tract Infection, Anaemia, Tremors
- Child Health & Nutrition / Paediatrics
- Obesity / Weight control & Safe Weight loss / Nutrition & Diet
- Depression / Anxiety / Insomnia & Stress Management
- Erectile Dysfunction medications / Sexually transmitted diseases (STD)
Public Health Preparedness Clinic
National University Health System Primary Care Network
Singapore Ministry of Health Chronic Disease Management Programme (CDMP)
The information provided in this website is for knowledge purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice.
Should you encounter any medical problem that you are unsure of, always consult your doctor or health care provider for assistance and medical advice.
MD International Medical Centre / MD International (Singapore) Pte Ltd
9 Taman Serasi #01-11, Botanic Gardens View
Tel : 65-6694-1661 Fax : 65-6694 1771
Email : contact@mdimc.sg
Clinic hours:
Monday to Friday: 9am-12.30pm / 2pm-6.30pm Saturday: 9.30am-1pm
*Last registration is 30mins before the closing time
Closed on Sundays & Public Holidays
- Cashless service with most International Insurance companies and Insurance Medical cards are accepted
- Japanese, English & Mandarin-speaking Doctors and Medical staff
Please contact us at Tel: 6694 1661 to make an appointment.
Please make an appointment for the following at Tel: 6694 1661:
* Health Screening / Blood Test
* Pre-Departure PCR Swab Test / Serology Testing
- 小型外科手术
- 健康检查/验血
- 皮肤科治疗
- 过敏测试
- 疼痛管理与治疗
- 疫苗接种
- 出发前 PCR 拭子检测
- 血清学检测
MBBS (Monash), B Med Sc (Hons) (Monash), Dip Pract Derm (Wales, UK)
The Chiropractic Association Singapore, Japan Chiropractic Register, American Chiropractic Association, California Chiropractic Association
Physiotherapy-trained NBCE The National Board of Chiropractic Examiners

MD (Duke-NUS), MRCPCH (Paed)(UK)
YAMAGATA Chihiro 山懸千尋
Registered Psychologist
MD International Medical Centre
- General Practice Family Medicine
- Minor Surgical Procedures / Laser Treatments
- Management of Chronic Diseases (Diabetes / Hypertension / Heart Disease / High Cholesterol Management)
- Pain Relief & Management (Joint pains, Knee Pain, Back Pain, Migraine, Sports Injuries)
- Shockwave Treatment / Deep Muscle Stimulator DMS Therapy
- Dermatology Treatments - Skin Problems (Eczema, Acne, Rash & Hives, Boils, Dermatitis, Pigmented or Dry Skin, Moles, Skin Tags, Corns & Calluses, Wart, Treatment of Insect Bites & Stings)
- Dermoscopy - Non-invasive Detection of Skin Cancer
- Allergies Test & Management / Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis / Asthma Management
- Vaccinations / Immunization (National Adult Immunisation Schedule / National Child Immunisation Schedule / Influenza)
- Infectious diseases & Virology (COVID-19, Dengue, Flu, Hepatitis B)
- Respiratory Medicine - Cough, Wheezing, Shortness of breath
- Eye Health / Ophthalmology (Conjunctivitis, Foreign body in the Eye)
- Ear Nose Throat / ENT Rhinoscopy (Nose Bleed-Epistaxis, Snoring & Sleep Apnoea, Vertigo & Dizziness, Removal of Ear Wax)
- Audiogram – Hearing test
- Personal Health (Stomach ache, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Heartburn, Treatment of Gout)
- Elderly / Senior Health (Arthritis)
- Men's Health
- Women's Health (Osteoporosis, Heavy Periods, Breast lumps, Urinary Tract Infection, Anaemia, Tremors)
- Child Health & Nutrition / Paediatrics
- Travel Health (Vaccinations / Travellers' Diarrhoea)
- Health Assessment, Screening & Management / Blood tests
- Pre-Employment check-up / Work Permit / Employment Pass / Student Pass / Driving License Check-up
- Obesity / Weight control
- Neurological Disorders / Dementia Screening
- Depression /
Anxiety Management
- Insomnia & Stress Management
· Injection for Supraspinatus or Bicipital Tendonitis / Epicondylitis / Trigger finger / Plantar Fasciitis
· Tendon Sheath Injection
· Excision of small Skin tumours / Lipomas / Nail bed / Ear lobe cysts / Meibomian cyst
· Removal of Skin sutures / Skin tags / Sebaceous cysts / Various foreign bodies / Corneal foreign body
· Liquid Nitrogen Therapy
· Treatment of Plantar Warts / Calluses / Corns / Ganglions
· Splinters under nails
· Olecranon and Pre-patellar Bursitis
· Ear syringing
· Embedded earring stud
Recent Articles
-
Arthritis in the Elderly
Apr 26, 24 10:14 PM
Arthritis means inflamed joints & the commonest type is osteoarthritis. Learn what the symptoms are & what treatment is available. -
Regular aerobic exercise is one of the best ways for healthy aging.
Apr 26, 24 10:12 PM
Brain aging is characterized by declines in cognitive function. Learn how to prevent MCI, dementia and neurodegenerative diseases eg Alzheimer's disease. -
MDIMC 鎮痛治療と管理 - 脊椎の健康 MDIMC PAIN RELIEF MANAGEMENT - SPINE HEALTH
Apr 26, 24 10:11 PM
痛みを和らげる治療とセラピー - 脊椎の健康 - 健康な背骨は、人間の健康を維持する上で重要な役割を果たします。背骨の3つの主な役割は、体を支える、動かす、神経を保護することです。PAIN RELIEF TREATMENT & THERAPY - SPINE HEALTH